If you’ve ever set up a TV, connected a security camera, or worked on any type of data transmission system, you’ve probably seen a coaxial cable. But what exactly is it? A coaxial cable is a specially designed electrical cable that carries high-frequency signals with low interference, thanks to its layered construction of conductor, insulation, shielding, and outer jacket.
Now, you might be wondering why coaxial cables are still relevant in 2025. With all the advances in fiber optics and wireless technology, it’s easy to overlook them. However, coaxial cables remain widely used because they are reliable, cost-effective, and incredibly versatile across many industries, from telecom and broadcast to automotive and smart home systems.
In this blog, I’m going to walk you through everything you need to know about coaxial cables. We’ll explore their structure, common uses, different types available, and some practical buying tips to help you make the right choice.
What Is a Coaxial Cable?
Coaxial cables may seem like just another type of wire, but they play a crucial role in how we transmit data, video, and signals with precision and reliability. Whether used in televisions, industrial machines, or advanced communication systems, coaxial cables are still trusted for their ability to reduce interference and maintain signal quality. So, what exactly is a coaxial cable, and how does it work? Let’s take a closer look.
What Is a Coaxial Cable? (Simple Definition)
A coaxial cable is a type of electrical cable that transmits high-frequency signals with minimal loss or interference. The word “coaxial” means that the cable has two main conductors sharing the same axis – a center wire and a surrounding shield – separated by insulation.
How Does a Coaxial Cable Transmit Signals?
Coaxial cables work by allowing electrical signals (usually radio frequency or digital signals) to travel along the center conductor, while the surrounding metal shield blocks external electromagnetic interference (EMI). The insulating layer keeps these parts separate and helps maintain signal integrity. This design makes coaxial cables ideal for long-distance or high-frequency transmission.
Visual: Coaxial Cable Cross-Section Diagram
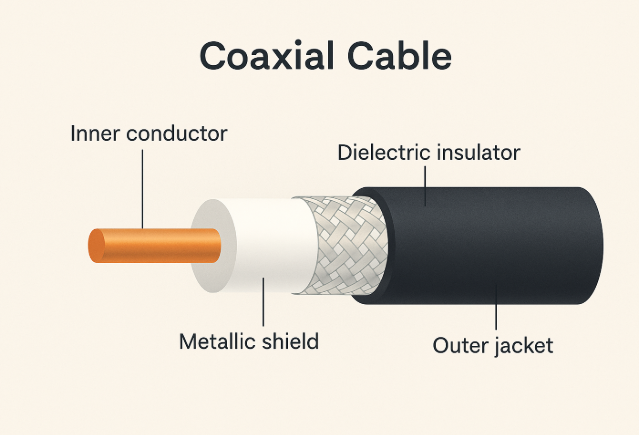
What Is the Structure of a Coaxial Cable?
Now that we understand what a coaxial cable is and how it works, let’s take a closer look at what makes its construction so reliable. Every part of a coaxial cable is carefully engineered to ensure strong, stable signal transmission even in noisy or demanding environments. Here’s a breakdown of its layered structure and why it matters.
What Is the Structure of a Coaxial Cable?
A coaxial cable is built with four main layers, each serving a specific purpose to protect the signal and minimize interference:
1.Core Conductor
At the center of the cable is the core conductor, usually made of solid or stranded copper. This is the path that carries the electrical signals. Copper is preferred because of its excellent conductivity.
2.Dielectric Insulator
Surrounding the core is the dielectric insulator, made from materials like foam polyethylene. This layer keeps the signal centered, maintains consistent spacing, and prevents energy loss or short circuits between layers.
3.Shielding Layer
Next comes the shielding, which is either a metal foil, braided copper mesh, or both. This layer blocks electromagnetic interference (EMI) from nearby cables, machines, or wireless devices, ensuring a cleaner signal.
4.Outer Jacket
The final layer is the outer jacket, typically made from durable plastic like PVC. It protects the internal components from moisture, abrasion, heat, and other physical damage.
Why This Layered Design Works
This precise, coaxial (same-axis) arrangement allows signals to travel efficiently down the cable with minimal signal loss, strong shielding, and high-frequency capability. Each layer supports signal integrity, especially in environments where external interference is a major concern.
Whether you’re dealing with surveillance cameras, industrial controls, or sensitive medical equipment, this structure makes coaxial cables a trusted solution for reliable performance.
What Are the Types of Coaxial Cables?
Although all coaxial cables have a similar basic structure, they are not all the same. The type you need depends on the application. For example, home video systems, industrial equipment, and precision electronics each require different levels of performance, flexibility, and shielding. Now let’s take a look at the most common types and see how they compare.
What Are the Types of Coaxial Cables?
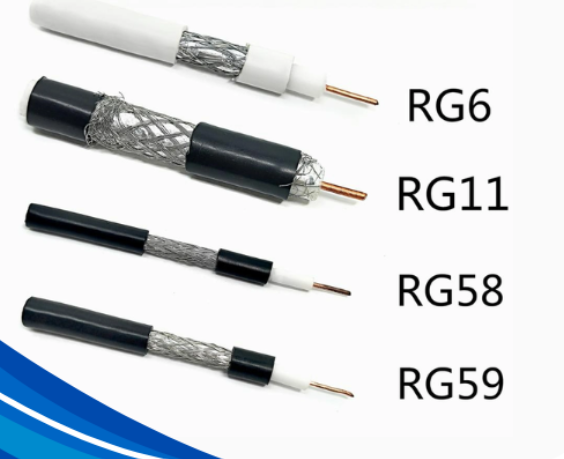
There are many types of coaxial cables, but these four are the most widely used across both consumer and industrial sectors:
| Type | Impedance | Core Size | Frequency Range | Best For | Pros |
| RG6 | 75 ohms | Thicker core | Up to 3 GHz | TV, Satellite, CCTV, Broadband Internet | Low signal loss, high-frequency support |
| RG59 | 75 ohms | Thinner core | Up to 1 GHz | Analog video, short-distance CCTV | More flexible, cost-effective |
| RG11 | 75 ohms | Thicker than RG6 | Up to 3 GHz+ | Long-distance signal transmission | Excellent low-loss performance |
| Mini Coax | 50/75 ohms | Very thin core | Varies | Compact devices, medical, RF modules | Ultra-flexible, space-saving design |
Quick Summary
- RG6 is the most versatile for modern use, offering strong shielding and low loss.
- RG59 is ideal for short-distance, lower-bandwidth applications.
- RG11 is perfect for long cable runs where maintaining signal strength is critical.
Mini coaxial cables are used in specialized environments like medical or high-density electronics where space is limited.

What Are the Common Applications?
Understanding how coaxial cables are used in the real world helps highlight just how essential they still are, even with today’s fast-evolving technology. Thanks to their strong shielding and ability to handle high-frequency signals with low loss, coaxial cables remain a key component across many industries. Let’s explore where and how they are most commonly used.
What Are the Common Applications of Coaxial Cables
Telecommunications
Coaxial cables are a backbone for transmitting television signals, broadband internet, and telephone connections. Their high-frequency handling and interference protection make them a reliable choice for telecom networks.
CCTV and Security Systems
In surveillance systems, coaxial cables like RG59 and RG6 are used to link cameras to DVRs and monitors. They provide stable video signals and are especially useful in analog and HD-over-coax setups.
Medical Equipment
Mini coaxial cables are perfect for medical devices where space is limited and signal clarity is critical. They are used in imaging systems, monitoring devices, and diagnostic tools.
Automotive and EV Systems
Modern vehicles rely on coaxial cables for infotainment systems, parking sensors, battery monitoring, and camera feeds. Their resistance to electromagnetic interference makes them ideal in electric and high-voltage systems.
Aerospace and Military
These cables are trusted for mission-critical systems such as radar, avionics, communication units, and navigation tools. Their durability and signal integrity meet strict military and aerospace requirements.
Industrial Automation
In smart factories and automated machinery, coaxial cables are used for data transmission in sensors, robotics, and control systems. Their rugged design withstands vibration, heat, and EMI-heavy environments.
What Are the Advantages of Coaxial Cables?
After learning about where coaxial cables are used, it’s easy to see why they’ve remained so popular for decades. But what exactly makes them stand out compared to other types of cables? From performance to practicality, coaxial cables offer a balanced combination of reliability, durability, and cost-efficiency that’s hard to beat.
What Are the Advantages of Coaxial Cables?
1.High Shielding Against EMI
One of the biggest advantages I appreciate about coaxial cables is their excellent protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI). Thanks to the metal shielding around the core conductor, these cables can transmit signals even in environments full of electrical noise such as factories, vehicles, or near power equipment without distortion.
2.Reliable Signal Over Long Distances
Coaxial cables are designed to maintain signal quality over extended lengths. Unlike some unshielded cable types, coax can carry high-frequency signals without significant loss, which makes it ideal for TV, satellite, and broadband data transmission. I’ve seen it perform well even in large building setups or long outdoor runs.
3.Durable and Cost-Effective
Coaxial cables are built to last. With a strong outer jacket and robust internal structure, they resist physical damage and environmental wear. At the same time, they’re relatively low-cost to produce and install, especially when compared to more complex fiber optic systems offering a great balance between performance and affordability.
4.Easy to Install and Terminate
Another thing I love about coaxial cables is how simple they are to work with. Whether you’re using crimp connectors, twist-on ends, or compression fittings, terminating a coax cable is quick and doesn’t require expensive tools. This makes them ideal for both DIY setups and large-scale professional installations.

What Are the Limitations or Disadvantages
While coaxial cables offer many advantages like durability and signal stability, no cable is perfect. It’s just as important to understand the limitations of coaxial cables especially if you’re comparing them to newer technologies like fiber optics or designing systems for long-term performance. From my experience, here are the main drawbacks to keep in mind:
What Are the Limitations or Disadvantages of Coaxial Cables?
1.Less Bandwidth Than Fiber Optics
Although coaxial cables are reliable for data and video transmission, they can’t match the bandwidth capacity of fiber optics. For applications requiring ultra-fast internet, large data transfer, or real-time high-resolution video streaming, fiber offers significantly higher speed and lower latency. If you’re planning for future-proof infrastructure, this could be a deciding factor.
2.Bulkier Than Some Alternatives
Compared to thinner cables like twisted pair or fiber strands, coaxial cables can be physically bulky and less flexible, especially types like RG11. This can make installation more difficult in tight spaces, especially in compact electronics or complex routing paths.
3.Can Degrade Over Time If Low-Quality Materials Are Used
Not all coaxial cables are created equal. If low-quality materials are used in the conductor, insulation, or shielding, the cable can degrade faster, leading to signal loss, corrosion, or even safety hazards. That’s why I always recommend sourcing from reliable manufacturers like Yihetai to ensure long-term performance.
Coaxial Cable vs. Other Cable Types
At this point, you might be wondering how do coaxial cables compare to other common cable types like twisted pair and fiber optics? I’ve worked with all three in different projects, and each has its strengths depending on the application. Let me show you how they differ in terms of performance, cost, and ideal usage scenarios so you can make the best choice for your needs.
Coaxial Cable vs. Twisted Pair vs. Fiber Optic Cable
| Feature / Cable Type | Coaxial Cable | Twisted Pair Cable (Ethernet) | Fiber Optic Cable |
| Signal Type | Electrical | Electrical | Light (optical) |
| Speed / Bandwidth | Moderate (up to ~10 Gbps for short distances) | Moderate to High (up to 10 Gbps for Cat 6+) | Very High (up to 100+ Gbps) |
| Distance (Signal Range) | Long (better than twisted pair) | Short to Medium (depends on category) | Very Long (up to several kilometers) |
| EMI Resistance | High (due to shielding) | Low to Medium (unshielded or shielded) | Very High (immune to EMI) |
| Flexibility | Medium | High | Low to Medium (depending on fiber type) |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | High |
| Installation Complexity | Easy | Very Easy | Complex (needs special tools & skills) |
| Best Use Cases | TV, CCTV, RF, Broadband Internet | LAN, Office Networking, VoIP | Data Centers, Long-Distance Networks, Telecom |
Best-Case Use Scenarios
Coaxial Cable: Best for high-frequency signals in environments with electrical noise, such as CCTV systems, broadband, or automotive radar.
Twisted Pair: Ideal for local networking (LAN), including home and office Ethernet setups.
Fiber Optic: Best for high-speed, long-distance, and interference-free data transmission, such as data centers, telecom backbones, or critical medical networks.

What Are the Manufacturing and Quality Standards for Coaxial Cables?
Coaxial cable performance depends on both high-quality materials and precise manufacturing. In critical fields like automotive, medical, and aerospace, meeting strict industry standards is essential for ensuring reliable signal transmission.
What Are the Manufacturing and Quality Standards for Coaxial Cables?
1.Industry Certifications
Coaxial cables used in professional or industrial applications should meet key certifications to ensure quality, safety, and compliance:
- ISO 9001: This international standard ensures that the cable manufacturer follows a consistent quality management system. It covers every stage from raw material inspection to final testing.
- UL Certification (e.g., UL E241405, E241406): UL ensures safety, fire resistance, and performance for electrical cables. It’s critical for products entering North American markets.
- IATF 16949: Specifically required for the automotive industry, this certification ensures the manufacturer meets rigorous quality standards in design, development, and production of automotive-grade coaxial cables.
2.Importance of Testing and Traceability
I always emphasize that cable testing is not optional it’s essential. Reliable manufacturers test for:
- Signal performance (impedance, attenuation)
- Shielding effectiveness (EMI resistance)
- Tensile strength and insulation resistance
- Continuity and appearance inspection
In addition, traceability systems ensure every batch or individual cable can be traced back to its production run, which is critical for quality assurance and after-sales service, especially in regulated industries like medical and defense.
Yihetai’s Custom Cable Capabilities (Optional)
At Yihetai, we don’t just manufacture coaxial cables we engineer them to meet your exact specifications. Backed by ISO 9001, UL, and IATF 16949 certifications, our cables are 100% tested and fully traceable. Whether you need high-frequency coax for EV systems or mini coaxial cables for compact medical devices, we deliver custom solutions with precision, speed, and reliability.
How to Choose the Right Coaxial Cable
With so many types of coaxial cables available, choosing the right one can feel overwhelming. But once you match the cable’s specifications to your actual application, the decision becomes much easier. Whether you’re working on a CCTV system, RF communication setup, or data transfer line, it’s important to consider factors like impedance, shielding, length, and connector types. Below is a practical guide to help you select the best coaxial cable for your needs.
How to Choose the Right Coaxial Cable
| Application | Recommended Type | Key Specs to Consider | Standard vs Custom |
| CCTV / Video | RG59 or RG6 | 75 ohms impedance, moderate shielding, BNC connectors | Standard is common, custom for longer runs |
| RF Communication | RG6, RG11, or RG142 | 50 ohms impedance, high shielding, SMA or N-type connectors | Custom advised for frequency and power needs |
| Internet / Data | RG6 or RG11 | 75 ohms, solid core, low-loss design, F-type connectors | Standard fits most home setups |
| Medical Equipment | Mini Coaxial | Compact size, EMI shielding, specialized connectors | Custom preferred for size and reliability |
| Automotive / EV | Shielded RG6-type | High EMI protection, durable jacket, vibration-resistant | Custom often required for harness integration |
| Aerospace / Military | RG400 or Mil-spec | High-temp tolerance, double shielding, rugged build | Always custom for compliance and performance |
Quick Tips
- Impedance: Match 50 or 75 ohms based on the system requirements.
- Shielding: Use double or braided shielding for noisy environments.
- Length: Longer cables require low-loss types like RG11.
- Connectors: Choose compatible connectors (BNC, F-type, SMA, etc.).
- Custom Needs: For tight spaces, harsh conditions, or high-performance systems, a custom cable from a manufacturer like Yihetai ensures perfect fit and function.
When Choose Custom Coaxial Cable Solutions
In many cases, standard coaxial cables from the shelf will do the job. But I’ve also seen plenty of situations where “good enough” just isn’t enough—especially when precision, durability, or integration with custom equipment is required. That’s where custom coaxial cable solutions come in. If you’re working on a complex system, a high-stakes industry, or just want maximum performance, custom cables can make all the difference.
When to Choose Custom Coaxial Cable Solutions
When Off-the-Shelf Isn’t Enough
Here are a few scenarios where I recommend going custom:
- Your system has unique size, length, or connector requirements
- You need extreme flexibility, waterproofing, or high-temperature resistance
- You’re combining multiple signals or power lines in a tight space
- The cable must meet strict safety, medical, or military standards
- You need to optimize for signal clarity, EMI shielding, or space constraints
If you’re dealing with any of these situations, a mass-produced cable may limit your design or worse, cause reliability issues.

Benefits of Working with a Custom Cable Manufacturer
From my experience, working with a reliable custom cable manufacturer brings several advantages:
- Tailored design based on your technical requirements and operating environment
- Improved reliability and signal quality, especially in challenging conditions
- Reduced waste and better fit, eliminating unnecessary cable length or unused features
- Stronger quality control, including 100% testing and full traceability
- Time and cost savings over the long term – less troubleshooting and fewer replacements
What Yihetai offers
At Yihetai, we focus on building custom coaxial cable solutions for industries such as automotive, medical, energy, and aerospace. With over 23 years of manufacturing experience, we handle every step in-house from design and material sourcing to production and testing. Whether your need is a prototype or a large-volume run, we deliver precise, durable, and cost-effective solutions tailored to your application.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve explored what a coaxial cable is, how it’s built, and why it remains so useful today, I hope you feel more confident in understanding its value. Coaxial cables are still widely trusted across many industries in 2025 thanks to their dependable signal transmission and flexible applications.
If your project requires something more specific than standard cable options, I suggest consulting a custom cable manufacturer like Yihetai. They have the experience and capability to design coaxial cable solutions tailored exactly to your technical and environmental needs.
If you have any questions or need advice on choosing the right coaxial cable, I invite you to leave a comment below or reach out directly. I’m always happy to help you find the perfect solution.


