Have you ever wondered how mechanics can quickly figure out what’s wrong with your car just by plugging in a small device? That’s the magic of OBD, or On-Board Diagnostics. It’s the system that allows your vehicle to “talk” and share vital information about its health. But not all OBD cables are the same – and choosing the wrong one can leave you confused or unable to access the data you need.
When I first started learning about vehicle diagnostics, I realized how crucial the OBD cable is – it’s the bridge between the car and the diagnostic tool. The problem is, there are two main types: OBD1 and OBD2, and they’re very different in design, usage, and compatibility.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through the key differences between OBD1 and OBD2 cables, so you can confidently choose the right one for your vehicle or project.
What Is OBD Cable?
Before diving into the differences between OBD1 and OBD2 cables, it’s important to first understand what an OBD cable is and why it plays such a critical role in automotive diagnostics. Whether you’re a mechanic, a car enthusiast, or someone simply trying to make sense of a check engine light, knowing the basics of OBD systems will help you appreciate how these cables work and why choosing the right type matters.
What Is an OBD Cable?
OBD, or On-Board Diagnostics, is a system built into vehicles that monitors the performance of various components – especially the engine and emissions system. When something goes wrong, the OBD system records fault codes and triggers the “check engine” light on your dashboard.
The main purpose of OBD systems is to provide real-time access to a vehicle’s health data. This includes information such as engine speed, fuel efficiency, sensor readings, and trouble codes that point to specific issues. It helps technicians quickly diagnose problems and reduces the time and guesswork involved in repairs.
An OBD cable is the physical link that connects the vehicle’s diagnostic port to a scan tool or computer. One end of the cable plugs into the vehicle’s OBD port (usually found under the dashboard), and the other end connects to the diagnostic device. Through this connection, data flows from the vehicle to the tool, allowing for accurate analysis, code reading, and sometimes even reprogramming of the car’s control modules.
What is OBD1 Cable?
Now that we understand what an OBD cable is and how it fits into a vehicle’s diagnostic system, let’s take a closer look at OBD1 cables, which represent the first generation of on-board diagnostic technology. To fully appreciate the advancements that came with OBD2, it’s important to understand how it all started.
What Is OBD1 Cable?
Origin and Purpose
The OBD1 system was introduced in the 1980s as the automotive industry’s initial effort to electronically monitor emissions and engine performance. It was created in response to growing environmental concerns and aimed to help reduce harmful emissions by detecting engine problems. However, the system was still quite basic compared to modern standards.
Manufacturer-Specific Standards
One major drawback of OBD1 was the lack of standardization. Each car manufacturer developed its own diagnostic system, meaning a cable or tool that worked on one brand would not be compatible with another. This made diagnostics more complicated for both car owners and mechanics.
Typical Connectors and Protocols
OBD1 cables used connectors that varied in shape, size, and pin configuration, depending on the manufacturer. Communication protocols were also unique to each brand. As a result, specific software and tools were required to read data from different vehicles.
Limited Data Access and Diagnostics
OBD1 systems provided access to only the most essential engine data. Diagnostic information was very limited, and real-time data was often unavailable. This made troubleshooting slower and less reliable than with newer systems.
Example Vehicles Using OBD1
Vehicles that used OBD1 include many models produced between the early 1980s and 1995. Common examples are:
- Toyota Corolla and Camry from 1984 to 1995
- Honda Accord and Civic from 1985 to 1995
- Chevrolet trucks and sedans from 1986 to 1995
- Ford Taurus and Ranger from 1990 to 1995
Each of these vehicles required a specific OBD1 cable to perform diagnostics properly.

What is OBD2 Cable?
After understanding the limitations of OBD1, it’s easy to see why the industry needed a more unified and advanced solution. That’s where OBD2 comes in. Developed as the next-generation system, OBD2 brought significant improvements in both functionality and standardization. Let’s explore what makes the OBD2 cable so essential in today’s vehicle diagnostics.
What Is OBD2 Cable?
Standardized System Introduced in 1996
OBD2 was officially introduced in the United States in 1996 as a government-mandated system for all cars and light trucks sold in the market. Unlike its predecessor, OBD2 was designed to follow strict standards for emissions control, performance monitoring, and diagnostics. This standardization greatly simplified vehicle maintenance and inspection.
Universal Protocols and Connectors
One of the most important features of OBD2 is its universal connector. All OBD2-equipped vehicles use the same 16-pin connector, typically located under the dashboard. The system supports multiple communication protocols, including CAN, ISO, and SAE standards, making it much easier for scan tools and diagnostic devices to work across different car brands.
More Comprehensive Diagnostics
OBD2 cables give access to a wide range of real-time data and trouble codes. From engine and transmission to fuel system and emissions components, OBD2 allows technicians to monitor vehicle health in detail. This deeper level of information enables faster, more accurate diagnostics and helps prevent serious problems before they occur.
Compatibility with Scan Tools and Software
Thanks to its standard interface, the OBD2 cable works with most modern scan tools, diagnostic devices, and even mobile apps. Whether you’re a professional mechanic or a car owner using a Bluetooth OBD2 scanner, the system allows easy access to your vehicle’s information without brand-specific equipment.
Example Vehicles Using OBD2
Any vehicle sold in the United States from 1996 onward is equipped with OBD2. Examples include:
- Toyota Corolla, Camry, and RAV4 from 1996 onward
- Honda Civic, Accord, and CR-V since 1996
- Ford F-150, Focus, and Escape models built after 1996
- Chevrolet Silverado, Malibu, and Tahoe from 1996 onward
These vehicles all support the 16-pin OBD2 interface, making diagnostics simpler and more consistent across different makes and models.

What Are The Pros And Cons Of OBD1 And OBD2 Cables?
Now that we’ve explored what OBD1 and OBD2 cables are, you might be wondering which one is better. The truth is, each type has its own advantages and drawbacks, especially depending on the age of the vehicle and the level of diagnostic detail required. Below is a quick comparison to help you understand the strengths and limitations of both OBD1 and OBD2 cables.
Pros and Cons of OBD1 and OBD2 Cables
| Feature | OBD1 Cable | OBD2 Cable |
| Introduction Period | 1980s–mid 1990s | 1996 and later |
| Pros | Designed for older vehicles – Simple fault code reading – Compatible with legacy systems | Universal 16-pin connector – Works on most vehicles post-1996 – Supports real-time data and advanced diagnostics |
| Cons | Manufacturer-specific connectors and protocols – Limited data and functionality – Requires different tools for each brand | Not compatible with pre-1996 vehicles – Can be more complex to troubleshoot at times |
| Connector Type | Varies by manufacturer | Standardized 16-pin connector |
| Diagnostic Capabilities | Basic fault codes only | Full diagnostics including live data, freeze frame, emissions readiness |
| Ease of Use | Less convenient, often brand-specific tools needed | Plug-and-play with most modern scanners |
| Vehicle Coverage | Older vehicles before 1996 | Most vehicles from 1996 to present |
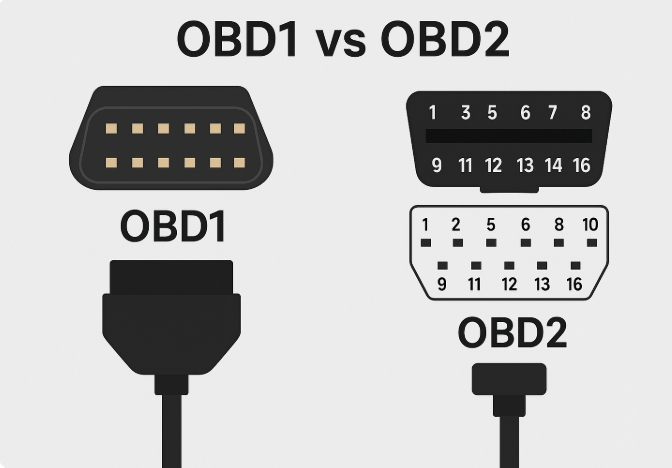
What Are The Connector And Pin Configurations Of OBD1 And OBD2 Cables?
Understanding the physical structure of OBD cables is just as important as knowing how they work. After all, the connector type and pin layout determine compatibility with vehicles and diagnostic tools. Let’s take a closer look at how OBD1 and OBD2 cables differ in terms of design, pin configurations, and why proper pin matching matters, especially when creating custom wiring harnesses.
Connector and Pin Configurations of OBD1 and OBD2 Cables
OBD1 Cable
Connector Type: OBD1 connectors were not standardized. Each car manufacturer designed its own connector shape, size, and pin arrangement. Some used 2-pin connectors, while others had up to 12 or more pins.
Examples:
- GM: ALDL 12-pin connector
- Toyota: 17-pin or 22-pin rectangular connector
- Honda: 3-pin connector
- Pin Configuration: Manufacturer-specific. No consistent layout across brands.
- Physical Design: Usually large, rectangular, or square with plastic casing and exposed or recessed pins.
- Drawback: A separate cable or adapter was needed for each brand, making diagnostics inconvenient for multi-vehicle workshops.
OBD2 Cable
- Connector Type: OBD2 introduced a universal 16-pin (J1962) trapezoidal connector that fits all compliant vehicles.
- Pin Configuration:
- Pin 4 and 5: Ground
- Pin 6 and 14: CAN High/Low (for modern protocols)
- Pin 7: K-Line (ISO 9141)
- Pin 16: Battery power (12V)
- Physical Design: Compact, durable, and universally shaped. Easily plugs into any post-1996 vehicle’s OBD2 port.
- Benefit: One cable works for most cars, making diagnostics faster and easier
Why Correct Pin Matching Matters for Custom Wiring Harnesses
When creating custom OBD cables or wiring harnesses, especially for specialized tools or aftermarket applications, precise pin mapping is critical. Incorrect pin connections can:
- Damage diagnostic tools or ECUs
- Lead to false readings or no communication
- Cause short circuits
That’s why manufacturers like Yihetai place high importance on accurate pin layout design, connector quality, and full electrical testing in every custom OBD cable we produce. Proper pin matching ensures safe, reliable, and efficient diagnostics every time.
What is the application of OBD cables in the automotive industry?
Now that we’ve explored the technical differences between OBD1 and OBD2 cables, let’s take a closer look at how these cables are actually used in the automotive world. From daily diagnostics in repair shops to large-scale fleet management systems, OBD cables play a critical role in keeping vehicles running safely, efficiently, and within legal standards.
Application of OBD Cables in the Automotive Industry
Now that we’ve explored the technical differences between OBD1 and OBD2 cables, let’s take a closer look at how these cables are actually used in the automotive world. From daily diagnostics in repair shops to large-scale fleet management systems, OBD cables play a critical role in keeping vehicles running safely, efficiently, and within legal standards.
Application of OBD Cables in the Automotive Industry
1.Role in Diagnostics and Vehicle Monitoring
OBD cables are essential tools in every modern workshop. They connect a vehicle’s diagnostic port to scan tools or computers, allowing mechanics to access real-time data such as engine temperature, RPM, fuel system status, and trouble codes.
Example: A mechanic diagnosing a 2015 Toyota Camry can use an OBD2 cable to quickly identify a faulty oxygen sensor that’s causing a check engine light, saving hours of manual inspection.
2.Usage in Emission Control and Compliance Testing
Government regulations require that vehicles meet strict emission standards. OBD systems monitor emission-related components and report any failure through diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). These can be read using an OBD cable during routine inspections.
Example: In California, vehicles undergo smog checks that involve connecting an OBD2 scanner via the cable to ensure no emission-related codes are present. If a vehicle has a bad catalytic converter, it will be flagged immediately through the system.
3.Importance in Fleet Management and Telematics
OBD cables are also integrated into fleet management systems, allowing businesses to track vehicle performance, fuel usage, idle time, and maintenance needs. These cables are often connected to GPS or telematics devices that send real-time data to cloud platforms.
Example: A logistics company with a fleet of delivery vans installs OBD2-enabled telematics devices. These devices use the cable to collect data on each vehicle’s engine health and driving behavior, helping the company optimize fuel usage, schedule maintenance, and reduce downtime.
In all of these cases, the quality and compatibility of the OBD cable make a big difference especially when working with custom or high-performance systems. That’s where reliable manufacturers like Yihetai come in, providing customized OBD cable solutions tailored for diagnostics, compliance, and smart vehicle integration.

How to Identify Which OBD System Your Vehicle Uses
1.Identify by Model Year
This is the easiest and most common way.
Step-by-step:
Step 1: Check the manufacture date on your vehicle’s label (usually found inside the driver’s side door frame or in the owner’s manual).
Step 2: Use the rule of thumb:
If your vehicle was made before 1996, it likely uses OBD1.
If your vehicle was made in 1996 or later, it is required to have OBD2 by law (especially in the U.S., EU, and other regions following emission standards).
Example: A 1994 Toyota Corolla uses OBD1, while a 1998 Honda Accord uses OBD2.
2.Check the Diagnostic Port
The shape and location of the port also help you determine the system.
Step-by-step:
Step 1: Look under the dashboard, near the steering column. That’s where most OBD ports are located.
Step 2: Identify the connector:
OBD1 ports vary by brand and may be located in the engine bay, under seats, or in side panels. They often have 2 to 12 pins and unusual shapes.
OBD2 ports always have a standardized 16-pin trapezoidal shape, located within 2 feet of the steering wheel.
Tip: If the port does not fit a standard 16-pin OBD2 connector, it’s likely OBD1.
3.Use Manufacturer Service Data
This method provides the most accurate confirmation.
Step-by-step:
Step 1: Check your vehicle’s owner’s manual or search the manufacturer’s website using your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
Step 2: Look for terms like “OBD1,” “OBD2,” or “SAE J1962” (which refers to OBD2 compliance).
Step 3: You can also call the dealership or a certified repair shop for confirmation.
Example: A technician uses the VIN to confirm that a 1996 BMW 3-Series was among the early models to switch to OBD2, even though it visually resembles an OBD1 setup.
What Are The Use Cases And Application Scenarios Of OBD1 And OBD2 Cables?
Now that we’ve covered how to identify your vehicle’s OBD system, let’s look at some practical scenarios. Whether you’re servicing a 1990s sedan or a brand-new hybrid SUV, the type of OBD cable you use makes a big difference. Here’s when to use OBD1 or OBD2 cables and how they’re applied across different automotive sectors.
Use Cases and Application Scenarios of OBD1 and OBD2 Cables
When to Use OBD1 Cables
Classic Vehicle Diagnostics: For cars built before 1996, especially vintage or collector models like a 1991 Ford Mustang or a 1994 Toyota Supra.
Retrofit Projects: In custom car builds or restorations, where retaining the original engine and ECU is essential.
Manufacturer-Specific Maintenance: When servicing older vehicles in workshops that specialize in brands like GM, Honda, or Toyota.
Example: A mechanic restoring a 1989 Chevrolet Camaro uses a GM 12-pin OBD1 cable to diagnose ignition timing and sensor issues.
When to Use OBD2 Cables
Modern Vehicle Maintenance: OBD2 cables are standard for diagnosing most vehicles from 1996 onward – covering everything from sedans to EVs.
Emissions Compliance Testing: Required in many countries to read OBD2 data during yearly smog or emissions checks.
Performance Monitoring: For real-time engine data, used by tuning specialists and performance shops.
Example: A technician at an inspection center connects an OBD2 cable to a 2018 Toyota RAV4 to verify all emissions systems are functioning properly before passing the vehicle.
Industries That Rely on OBD Cables
| Industry | Use Case |
| Automotive Repair | Reading/clearing trouble codes, sensor testing, component diagnostics |
| Emissions Testing | Monitoring emissions readiness status, verifying compliance |
| Fleet Management | Real-time GPS, fuel efficiency tracking, predictive maintenance alerts |
| Car Rental/Leasing | Mileage tracking, engine performance monitoring, wear-and-tear alerts |
| Tuning & Motorsports | Real-time data logging, performance tuning, ECU programming |
No matter the scenario, choosing the correct cable type and using a reliable custom wiring solution can make diagnostics faster, safer, and more accurate. At Yihetai, we provide OBD1 and OBD2 cables tailored to your specific application, ensuring seamless integration and high performance in any environment.
Why Custom OBD Cable Manufacturing with Yihetai?
After learning about the differences and applications of OBD1 and OBD2 cables, the next step is knowing where to find the right cable, especially when you need something custom. This is exactly where Yihetai stands out. With over twenty years of experience in the wiring harness industry, Yihetai offers reliable and fully customized OBD cable solutions that meet the specific needs of modern and legacy automotive systems.
Why Choose Yihetai for Custom OBD Cable Manufacturing
Expertise in Both OBD1 and OBD2 Cable Production
Yihetai has the capability to design and produce OBD1 cables for older vehicles as well as OBD2 cables for newer models. Whether you need a special connector layout or a durable cable built for repeated use, our team can deliver exactly what you require.
Precision Molding and Connector Matching
Each cable is crafted using precise molding techniques to ensure accurate connector fitting. Our team carefully matches each pin configuration to your specifications and tests every cable for electrical performance, strength, and durability.
Support for OEM and ODM Projects
Yihetai supports both original equipment manufacturers and developers of aftermarket diagnostic tools. We provide custom development, private labeling, and technical support throughout the process, helping our clients bring new products to market quickly and effectively.
Certified Quality You Can Trust
Yihetai operates under strict international standards. Our production is certified under ISO 9001 and IATF16949, which guarantees high quality and full traceability. We use only premium materials to ensure safety, stability, and long-term performance.
Choosing Yihetai means gaining a dependable partner who understands your technical needs and delivers tailor-made solutions with confidence and care. Let us help you build the right OBD cable for your project.
Conclusion
After comparing OBD1 and OBD2 cables, it is clear that OBD2 has become the go-to standard for modern vehicle diagnostics. While OBD1 was an early step in automotive technology with manufacturer-specific connectors and limited data, OBD2 offers a universal interface, standardized protocols, and real-time access to critical performance data. It is easier to use, compatible across most vehicles made after 1996, and supports a wide range of scan tools.
From my experience, OBD2 is not just more advanced. It is essential for accurate, fast, and efficient diagnostics in today’s vehicles.
That is also why I believe using a high-quality custom OBD cable can make all the difference. At Yihetai, we design and manufacture custom OBD cables that meet specific technical and environmental requirements. This helps technicians and engineers work smarter and more efficiently.


