Cables are the hidden lifelines of every piece of consumer electronics we use from smartphones and laptops to gaming consoles and home appliances. But with so many types of cables out there, it can be confusing to choose the right one for your setup.
One question I often get is: Should I go with flat cables or round cables? Each design has its own benefits and drawbacks. Flat cables offer flexibility and a slim profile perfect for tight spaces, while round cables are known for durability and shielding performance. But choosing the wrong type could lead to inefficiencies, unnecessary costs, or even technical issues.
In this blog, I’ll break down the pros and cons of flat and round cables based on real-world applications. My goal? To help you confidently select the best cable solution for your specific needs whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a product designer, or just upgrading your setup at home.
What Are Flat Cables?
When I talk about flat cables, I think about how important they’ve become in the world of modern electronics. As our devices get thinner and more compact, flat cables have become essential for efficient and flexible wiring. They really help save space and improve reliability in tight spaces.
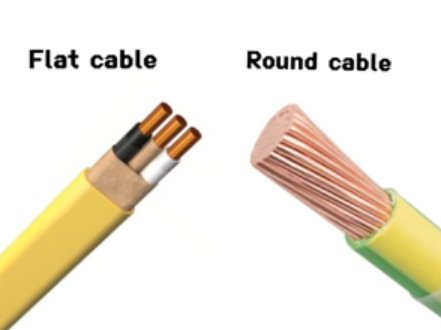
Flat cables are electrical cables with conductors arranged side by side in a flat, ribbon-like configuration, rather than bundled in a round form. This design allows for compact layouts, consistent electrical performance, and easy bending in limited spaces. Each conductor is typically equally spaced, providing a straight and orderly path for the electrical signals. Flat cables also often feature a flexible plastic insulation base with metallic conductors bonded to one side. Many flat cables are referred to as flexible flat cables (FFC), especially when used in high-density or compact electronics like laptops and cell phones.
Common Manufacturing Materials
Flat cables use a variety of materials depending on their application and needed properties:
- Conductors: Most commonly made from copper bare, tin-plated, or gold-plated for enhanced performance and corrosion resistance.
- Insulation: Polyester and polyimide tapes are popular for insulation due to their flexibility, flame resistance, and durability. Some specialized cables use PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) for even higher resistance to temperature, chemicals, and electrical stress.
- Jacket: The outer layer is often made from flexible PVC or other plastic materials to ensure protection and ease of installation while maintaining the thin profile.
Examples of Consumer Electronics Using Flat Cables
Flat cables are widely used in many consumer devices because of their compactness and reliable connections:
- Smartphones and Tablets: Used for internal connections between display, camera modules, and main boards.
- Laptops and Ultrabooks: Flat cables handle interfaces like keyboards, touchpads, and display connections.
- Digital Cameras and Camcorders: Internal wiring for moving parts and sensors.
- Gaming Consoles and Controllers: Linking internal modules efficiently in tight areas.
- Smartwatches and Fitness Trackers: Essential for compact wearable designs.
- Home Appliances: Devices like washing machines and microwaves also utilize flat cables for reliable, flexible connections
Flat cables play a major role in enabling today’s sleek and high-performing electronics, offering unparalleled flexibility, reliability, and space management.

What Are Round Cables?
When I think about round cables, I see them as the traditional backbone of electrical wiring in both industry and consumer electronics. These cables have been the go-to solution for transmitting power, data, and signals, especially where durability, flexibility, and effective shielding are essential. Round cables remain an integral part of how most of our everyday electronic devices stay connected and function seamlessly.
Round cables are traditional electrical cables where multiple insulated conductors are bundled together and surrounded by a cylindrical outer sheath. Inside, the wires may be twisted or layered to reduce interference and enhance mechanical strength. The circular design allows for comprehensive shielding, making round cables ideal for protecting signals against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and physical stress. This structure helps maintain consistent performance, even when cables are subject to bending, pulling, or harsh environmental conditions.
Common Manufacturing Materials
Round cables are typically made from the following materials:
- Conductors: Most commonly copper, sometimes tinned or silver-plated for added corrosion resistance and conductivity.
- Insulation: Each individual wire is insulated, often using materials like PVC (polyvinyl chloride), PE (polyethylene), or Teflon for high-temperature applications.
- Sheath: The outer jacket is usually made from flexible yet tough plastics such as PVC, thermoplastic elastomer (TPE), or rubber compounds, providing protection from mechanical damage and environmental exposure.
- Shielding (optional): Many round cables include foil or braided shielding to guard against EMI and cross-talk, which is especially important in data transmission and sensitive settings.
Examples of Consumer Electronics Using Round Cables
Round cables are widely used across a vast array of consumer electronics due to their durability and shielding capabilities. Examples include:
- Power cords for laptops, monitors, and televisions: Ensures reliable delivery of electrical power.
- USB and HDMI cables: Used for high-speed data, video, and audio transfer between devices.
- Audio cables (aux, headphone, speaker cables): Provide quality signal delivery and layout flexibility.
- Network (Ethernet) cables: Traditional round Ethernet cables are staples for wired internet connections.
- Charging cables for various portable devices: From smartphones to wearables, many rely on round charging cords for their resilience and long lifespan.
- Peripheral connectors for printers, external hard drives, cameras, and more: Used in numerous consumer gadgets that need steadfast and interference-free connections.
Round cables continue to be the go-to solution whenever durability, shielding, and secure long-distance connections are high priorities in electronic device design.
What Are the Key Differences Between Flat Cables and Round Cables?
Before choosing the right cable for your consumer electronics project, it’s essential to understand how flat cables and round cables ifferences in form and function. While both are used to transmit signals or power, their structural design has a direct impact on performance, installation, and cost.
Here is a detailed comparison of the key differences between flat cables and round cables presented in a table format:
| Feature | Flat Cables | Round Cables |
| Physical Structure & Design | Conductors arranged in a single flat layer; ribbon-like shape | Conductors bundled together in a circular cross-section |
| Flexibility & Bend Radius | Flexible in one direction; ideal for folding or layering | More flexible in multiple directions; better for dynamic or twisting motion |
| Durability & Wear Resistance | May wear faster under repeated multi-directional bending | More robust; better suited for rugged or high-motion environments |
| Weight & Space Requirements | Lightweight and space-efficient; fits into slim or tight enclosures | Heavier and bulkier; requires more space for installation |
| Manufacturing Complexity & Cost | Simple structure; cost-effective for standard designs | More complex due to shielding, jacketing, and fillers; typically more expensive |
What Are the Advantages of Flat Cables?
Once we understand how flat cables differents from round ones, it’s easy to see why they’ve become a popular choice in modern electronics. Their unique form factor not only simplifies cable routing but also brings several performance and design advantages that are hard to ignore. Let’s take a closer look at why flat cables are often preferred in space-conscious and precision-driven applications.
Flat cables have gained popularity in many electronic applications due to their unique design and several notable advantages. These advantages make them especially well-suited for compact and high-density electronic environments where space, airflow, and signal integrity are critical considerations.
Here are the key advantages of flat cables:
| Advantage | Explanation |
| Space-saving in compact devices | Flat cables have a slim, ribbon-like design that occupies significantly less vertical and overall space compared to round cables. This makes them ideal for use in tight, compact devices like smartphones, tablets, and wearables where every millimeter counts. |
| Better airflow in enclosed spaces | The flat profile allows cables to lie more closely to surfaces and not obstruct airflow as much as bulkier round cables. This improved airflow helps with cooling within densely packed electronic enclosures, contributing to better thermal management and system reliability. |
| Easier to manage in certain layouts | Flat cables can be routed neatly and stacked or layered with minimal wasted space, making cable management simpler in complex assemblies. Their flexibility in bending in one plane enables easier installation in tight or convoluted spaces without tangling or kinking. |
| Reduced signal interference in some designs | The consistent spacing of conductors within flat cables helps minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between signals. This controlled geometry supports better signal integrity, especially valuable in high-speed data transmission applications. |

What Are the Advantages of Round Cables?
While flat cables offer many benefits for compact and organized setups, round cables remain the preferred choice in many industrial and high-performance applications. Their layered structure and circular shape provide specific advantages that are hard to match in certain environments and use cases.
Round cables offer a range of advantages that make them a preferred choice for many consumer electronics, especially in environments demanding durability, strong signal transmission, and ease of installation in complex setups.
| Advantage | Explanation |
| Stronger outer protection for harsh environments | Round cables have a robust, thick outer jacket and internal fillers that provide enhanced mechanical strength. This makes them highly resistant to abrasion, crushing, and environmental hazards, suitable for use in industrial settings or outdoor conditions. |
| Better for long-distance signal transmission | The cylindrical construction enables better shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) which preserves signal integrity over longer distances, important for data cables and communication lines. |
| Easier to bundle and route in certain applications | Their round shape allows for straightforward bundling, pulling through conduits, and installation in cable trays where cables need to be grouped or run alongside other wiring infrastructures. |
| Widely available and cost-effective | Round cables are manufactured in large volumes with mature production technologies, resulting in broad availability and typically lower costs per unit, especially for standard power, audio, and network cables. |
What Are the Common Applications of Flat and Round Cables in Consumer Electronics?
Understanding where and how flat and round cables are commonly used can help you decide which type best suits your needs. In consumer electronics, each cable type is chosen based on performance requirements, space constraints, and environmental conditions. Let’s explore the typical applications where flat and round cables are used effectively.
Common Applications of Flat Cables
Flat cables, with their thin and flexible design, are predominantly used in compact, high-density electronic devices where space optimization and flexibility are essential. These cables connect various internal components efficiently within tight spaces.
- Laptops, Notebooks, and Tablets: Used for keyboard connections, display screens, touchpads, and other internal module connections where space is at a premium.
- Smartphones and Digital Cameras: Facilitate connections between displays, buttons, cameras, and batteries.
- Printers and Scanners: Employed to connect moving parts and electronic modules while allowing smooth mechanical movement.
- Flat Panel Displays and Monitors: Used inside LCD, LED, and plasma panels to connect screens to driver circuits.
- Home Appliances: Applied in devices like microwaves, washing machines, and smart home gadgets to connect control panels and sensors.
- Automotive Electronics: Connect displays, sensors, and control units within vehicles where vibration resistance and compact design are vital.
Common Applications of Round Cables
Round cables are widely used in applications where durability, shielding, and ease of installation are prioritized over space savings. Their robust design supports longer cable runs and environments that demand extra protection.
- Power Cords and Chargers: Round cables are the standard for power delivery in laptops, monitors, TVs, and mobile device chargers.
- Audio and Video Equipment: Aux cables, HDMI, speaker wires, and microphone cables often use round designs for reliable signal transmission.
- Network Connections: Ethernet cables predominantly have round structures to ensure shielding and performance over longer distances.
- Peripheral Devices: Used for printers, external hard drives, gaming controllers, and other gadgets requiring dependable connections.
- Industrial and Outdoor Consumer Equipment: Preferred in ruggedized products and appliances exposed to harsher conditions for resistance and longevity.
How to Choose the Right Cable for Your Needs
With so many cable types available, choosing the right one for your application can seem overwhelming. But by focusing on bellow 4 keys factors, you can confidently select a cable that not only fits your technical requirements but also performs reliably over time. Here’s what I always recommend evaluating before making a decision.
1.Consider Device Size and Available Space
If your device has limited internal space or a compact form factor, flat cables are often the better choice. Their low profile allows for neat, organized routing without taking up unnecessary room. Round cables, while more durable, may not be suitable in tight spaces due to their bulk.
2.Evaluate Flexibility and Movement Requirements
Think about how much movement or bending the cable will experience. Flat cables work well in static layouts or hinged devices that need to fold. Round cables are better for applications involving frequent motion or rotation, as they provide uniform flexibility in all directions.
3.Check Environmental Conditions (Heat, Vibration, Moisture)
The operating environment plays a big role in cable selection. In areas exposed to high temperatures, mechanical vibration, or moisture, round cables with layered insulation offer better protection and longer lifespan. Flat cables may need additional shielding or reinforcement in such conditions.
4.Budget and Availability Factors
Finally, consider your budget and sourcing timeline. Flat cables may be more cost-effective in standard configurations, especially for mass production. Round cables are widely available and offer a broader range of off-the-shelf options, which can help reduce lead times and overall cost in certain projects.
What Are the Future Trends in Cable Design for Consumer Electronics?
As consumer electronics continue to evolve, so do the technologies that connect their internal components. Cable design is no longer just about power and signal—it’s about meeting the demands of smaller devices, faster speeds, and tougher environments. Looking ahead, several trends are shaping the future of cable development in the electronics industry.
The future of cable design for consumer electronics is being shaped by ongoing advancements and evolving demands in technology, device miniaturization, and connectivity needs. As electronic devices become smaller yet more powerful, cable design must adapt to support high performance while fitting increasingly compact spaces. Here are 3 keys trends driving the future of cable design in consumer electronics:
1.Growth of Compact Devices Driving Flat Cable Adoption
As devices like smartphones, wearables, and ultrathin laptops continue shrinking, flat cables are increasingly favored. Their slim, ribbon-like profiles save critical space inside devices, allowing for more streamlined and lightweight products. This trend is expected to accelerate as manufacturers push for sleeker, more integrated designs.
2.Advances in Materials Improving Both Cable Types
Innovations in advanced materials are leading to cables with enhanced flexibility, durability, and thermal resistance. New insulating polymers, conductive coatings, and nanomaterial-infused components improve performance by providing stronger, lighter, and more reliable cables. These advances benefit both flat and round cables, enabling higher data rates and longer lifespans.
3.Potential Shift Towards Wireless but Continued Need for High-Quality Cables
While wireless technologies are growing, there remains a strong demand for wired connections for charging, high-speed data transfer, and internal device communications. Cables will continue to play a vital role, with future designs focusing on smart functionality, improved energy delivery, and integration with hybrid wired-wireless ecosystems.
How yihetai Support Both Flat Cable and Round Cable?
At Yihetai, we understand that both flat and round cables have unique roles in consumer electronics, and our expertise ensures we can provide the right solution for either type. From design to production, we work closely with customers to match cable technology with application requirements.
Custom Cable Assembly Solutions for Both Formats
We design and manufacture cable assemblies that integrate seamlessly with either flat or round cables, ensuring optimal performance, durability, and ease of installation.
Engineering Support for Performance and Compatibility
Our in-house engineering team provides guidance on conductor layout, insulation materials, and shielding methods to maximize performance and ensure compatibility with your devices.
Quality and Compliance Across All Cable Types
Whether working with flat or round cables, our products meet strict industry standards such as ISO, UL, and RoHS, giving customers confidence in safety and reliability.
Conclusion
After comparing flat cables and round cables, it’s clear that each type comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. Flat cables are compact, flexible, and great for space-saving installations, while round cables offer better shielding, durability, and are ideal for longer distances or more demanding environments.
From my experience, the best choice always comes down to the specific needs of your application. If you are working with limited space or need clean routing, flat cables are often the smarter option. If you need high performance, better signal protection, or robust handling, round cables may be the better fit.
Still unsure which cable suits your design best? I’m here to help. At Yihetai, we specialize in matching the right cable systems for any electronic setup. Contact us today for expert guidance and customized solutions tailored to your project.


