In the world of electronics, reliable cable termination is the backbone of smooth power delivery and data transmission. A poor connection can lead to signal loss, device malfunction, or costly downtime, which is something no engineer or manufacturer wants to face.
This is where IDC, or Insulation Displacement Contact technology, becomes a valuable solution. Instead of relying on the slower and more error prone process of stripping wires and soldering, IDC connectors pierce through the insulation to create secure electrical contact in a single step. This method not only speeds up production but also ensures consistent and high quality connections across large volumes of assemblies.
From my experience, IDC termination is a true game changer for modern cable assemblies. Whether in computers, telecom systems, or industrial equipment, it delivers efficiency, reliability, and cost savings. In this article, I will share everything you need to know about IDC cable termination and why it is essential in today’s electronics.
What Is IDC Cable Termination?
IDC (Insulation Displacement Contact) cable termination is a method of connecting electrical wires without the need to strip their insulation before making contact. Instead of manually removing insulation, IDC connectors have sharp metal blades or teeth designed to pierce through the insulation layer and establish a direct electrical connection with the conductor underneath.
Unlike traditional cable termination methods such as soldering or crimping which require stripping wires and either melting solder to fuse connections or mechanically compressing a connector around a bare conductor IDC termination simplifies and speeds up the process by eliminating the stripping step. This not only saves time but also reduces the chance of damaging delicate wires.
In practice, an IDC connector forces its blades through the insulation in one smooth action as the wire is inserted or the connector is pressed down. This piercing displaces the insulating material without needing to remove it, creating a secure, gas-tight connection that resists oxidation and vibration. The result is a reliable and efficient electrical contact that can be made quickly, often with simple hand tools or automated equipment.
IDC technology is widely used in ribbon cables and telecommunications wiring due to its efficiency and consistency, especially when multiple connections need to be made simultaneously. Its ability to deliver fast, reliable termination without stripping or soldering has made IDC a popular choice in various electronics and networking applications.
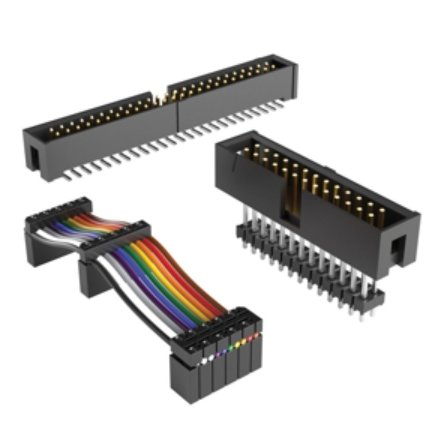

How IDC Cable Termination Works?
Understanding how IDC cable termination works can help you see why it’s a preferred solution in many electronic and industrial applications. The process is designed for speed, accuracy, and consistency, especially when dealing with multi-conductor ribbon cables. Here’s a closer look at how it all comes together.
IDC (Insulation Displacement Contact) cable termination is a highly efficient method used to connect wires without the need for stripping insulation. Here’s how the IDC termination process works in detail:
Step-by-Step Explanation of the Termination Process
Prepare the Ribbon or Multi-Conductor Cable
Start by removing the outer sheath of the cable with a sheath removal tool, exposing the individual insulated wires or ribbon conductors. The length of the stripped section depends on the connector specification but is typically just enough for the connectors to engage the wires properly.
Arrange and Align the Wires
The individual wires or pairs are separated and aligned according to the color-coding scheme that matches the IDC connector pinout. Care is taken to maintain the twist in twisted pair cables as close as possible to the termination point to reduce signal interference.
Position the Cable into the IDC Connector
The cable is carefully placed into the IDC connector’s slots, which have sharp metal contacts designed with a narrow slit.
Press or Punch Down the Connector
Using a specialized press tool, punch-down tool, or press machine, the cable is pressed firmly into the IDC connector. The metal slot blades pierce through the wire insulation and make direct contact with the conductor, all in one action.
Trim Excess Wire
As the tool punches down, it typically trims off any excess wire protruding beyond the connector to create a neat and compact termination.
Components Involved
Ribbon Cable or Multi-Conductor Cable: The cable that carries the signals, often with individually insulated wires aligned flat or in pairs.
IDC Connector: Contains U-shaped metal contacts or terminals with sharp edges designed specifically to cut through insulation and contact the conductor inside.
Press or Punch-Down Tool: The tool or machine that applies measured pressure to seat the cable fully into the IDC connector.
Manual vs Semi-Automatic IDC Assembly
Manual IDC Termination involves using handheld punch-down tools or simple presses. It requires some operator skill but offers flexibility for smaller runs or field work.
Semi-Automatic IDC Assembly uses mechanized presses or automated machines that control insertion depth and force precisely, improving consistency and speed ideal for mass production in factories.
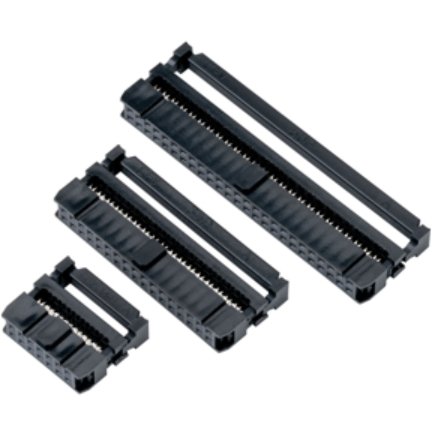

What Are the Common Types of IDC Connectors?
IDC connectors come in a variety of styles to suit different applications, wire counts, and board interfaces. The right choice depends on the type of cable you’re using and the electrical or mechanical needs of your device. Below are some of the most commonly used IDC connector types in consumer electronics and industrial systems.
What Are the Common Types of IDC Connectors?
1.Ribbon Cable Connectors
These are the most widely recognized IDC connectors and are specifically designed for flat ribbon cables. They allow multiple conductors to be terminated at once, making them ideal for compact, organized connections in computers, printers, and control panels.
2.Box Headers and Sockets
Box headers are male IDC connectors typically mounted on a PCB. They are used together with IDC sockets that connect to ribbon cables, creating a plug-and-play solution for board-to-cable assemblies. They are common in embedded systems and industrial electronics.
3.D-sub IDC Connectors
These connectors combine the D-sub interface (such as DB9 or DB25) with IDC technology for quick cable assembly. They are often used for serial communication, such as RS-232, and allow efficient termination of multiple signal wires to a standard interface.
4.Dual-Row IDC Connectors
Dual-row connectors feature two parallel rows of contacts, allowing higher pin counts in a relatively small footprint. These are useful in situations where you need to connect more signals without taking up too much space on the board.
5.Application-Specific IDC Connectors
Some IDC connectors are custom-designed for specific industries or equipment. These can include keyed connectors for safety, high-density IDC blocks, or connectors with additional shielding for EMI-sensitive environments. They are often used in automotive, medical, or telecom applications.
What Are Advantages of IDC Cable Termination?
In the world of modern cable assembly, especially for flat ribbon cables, IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) technology has become a highly preferred solution due to its speed, efficiency, and reliability. At Yihetai, where we specialize in custom wire harness manufacturing, IDC termination is often used in high-volume production environments across sectors like industrial electronics, computers, and appliances. Below are 5 keys advantages that make IDC cable termination an excellent choice:
1.Fast and Efficient for High-Volume Production
IDC cable termination enables rapid assembly without requiring traditional wire stripping or soldering. This speed is particularly beneficial for large-scale production lines, where thousands of terminations need to be completed with consistent quality and minimal downtime. Automation compatibility further enhances throughput and productivity, making it a top choice for manufacturers needing scale.
2.No Need to Strip Wires
One of the core benefits of IDC connectors is that the insulation on the wire does not need to be stripped manually. The IDC terminal features sharp blades that automatically cut through the insulation and make a solid electrical contact with the conductor during insertion. This eliminates an entire step in the production process, reducing errors and time consumption.
3.Consistent, Reliable Connections
IDC terminations provide uniform pressure and contact points, ensuring high-quality and repeatable connections. This reduces the risk of weak contacts, poor continuity, or performance degradation over time. Such consistency is critical in applications where reliability is non-negotiable, such as in automotive electronics or control systems.
4.Ideal for Multi-Conductor Flat Ribbon Cables
IDC technology is particularly well-suited for flat ribbon cables with multiple conductors. The connector can terminate all wires in one simple action, aligning perfectly with the parallel structure of the ribbon cable. This makes it a standard solution in computer and communication systems where space and signal integrity are key factors.
5.Lower Labor Cost in Assembly
By simplifying the assembly process and reducing manual tasks such as stripping, soldering, or crimping, IDC cable termination significantly lowers labor costs. Fewer steps mean less handling and reduced training time for operators. This cost-effectiveness is valuable in competitive industries requiring lean manufacturing strategies.
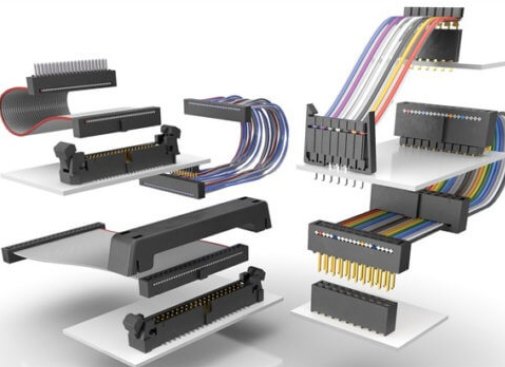
What Are the Limitations and Key Considerations of Using IDC Connectors?
While IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) technology offers significant benefits in speed, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, it’s important to understand its limitations and the specific scenarios where it may not be the most suitable solution. At Yihetai, we always evaluate the application requirements before recommending IDC termination to ensure long-term performance and customer satisfaction. Below are 3 keys limitations and considerations when working with IDC connectors:
1.Not Ideal for High-Vibration or High-Current Environments
IDC connectors are not typically designed for applications involving heavy mechanical stress or high electrical loads. In high-vibration environments such as automotive engines, industrial machinery, or aerospace systems IDC connections may loosen or degrade over time. Similarly, they are not well-suited for carrying high currents, as the contact points may heat up or lose integrity under excessive load. In such cases, crimp or soldered connections offer greater mechanical and electrical stability.
2.Limited Flexibility with Conductor Types and Sizes
IDC connectors are optimized for specific types of conductors, usually solid or stranded wires of certain gauges. They are not compatible with all wire types or insulation materials. Using wires outside the recommended specifications may result in poor contact, increased resistance, or even connector damage. For custom harness projects with mixed conductor types or special insulation (such as high-temperature or medical-grade wires), other termination methods may be more appropriate.
3.Requires Precision During Assembly
Although IDC assembly is fast, it requires a high degree of precision during the insertion process. Misalignment or improper seating of the wire can lead to incomplete connections or intermittent signal failures. Unlike traditional crimping or soldering, IDC doesn’t leave much room for adjustment once terminated. Therefore, trained personnel or precision tooling is necessary to ensure each termination is accurate and reliable, especially in automated high-speed production environments.

Where Is IDC Cable Termination Used?
IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) cable termination is a highly efficient method widely used in applications that demand fast, compact, and cost-effective connections. Because of its ability to quickly and reliably connect multiple conductors especially in ribbon cable assemblies it has become a preferred choice across various industries. At Yihetai, we frequently use IDC termination in several sectors where space, signal integrity, and production speed are key.
IDC cable termination is widely used across various industries and applications where reliable, fast, and efficient wiring connections are essential. Common usage areas include:
- Telecommunications and Networking: IDC connectors are prevalent in telephone systems, data networks, and patch panels. They facilitate rapid termination of flat ribbon cables for connecting multiple lines simultaneously.
- Consumer Electronics: Common in computers, printers, and other peripherals where internal ribbon cables connect circuit boards and components efficiently.
- Industrial Automation: Used for control systems, PLC wiring, and industrial machinery, IDC cabling provides reliable interconnections in complex setups.
- Automotive Systems: Employed in automotive electronics for control units, infotainment systems, and sensor wiring where quick, consistent terminations are needed.
- Medical Devices: Utilized in patient monitoring equipment and diagnostic machines, IDC connectors provide compact and dependable connections.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IDC termination supports wiring in small, space-constrained smart devices, including security systems, smart meters, and vending machines.
Why IDC Works So Well with Flat Ribbon Cables?
Flat ribbon cables are widely used in electronics, automation, and embedded systems due to their compact structure and ability to carry multiple signals in parallel. When it comes to terminating these cables quickly and reliably, IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) technology is the ideal match. At Yihetai, we often recommend IDC connectors for ribbon cable assemblies because of their perfect compatibility and production efficiency. Here’s why IDC works so well with flat ribbon cables:
1.Consistent Conductor Spacing
Flat ribbon cables are designed with uniformly spaced parallel conductors, which align precisely with the contact blades of IDC connectors. This perfect alignment ensures that each wire is terminated in the correct position without manual adjustment, providing reliable and consistent electrical contact across all conductors. It also reduces the risk of miswiring, making it ideal for data transmission and signal integrity.
2.Easy Mass Termination
One of the key advantages of IDC with flat ribbon cables is the ability to terminate all conductors at once in a single pressing operation. This mass termination process eliminates the need for stripping and individual crimping or soldering of wires. It drastically reduces assembly time and labor costs, making it ideal for high-volume production where speed and consistency are essential.
3.Space-Saving Layout for Compact Designs
Flat ribbon cables combined with IDC connectors offer a low-profile and highly organized wiring solution. This is especially beneficial in compact electronics, such as laptops, medical devices, or LED systems, where internal space is limited. The flat geometry of the cable and the compact IDC connector help minimize clutter, improve airflow, and maintain a clean and efficient internal layout.
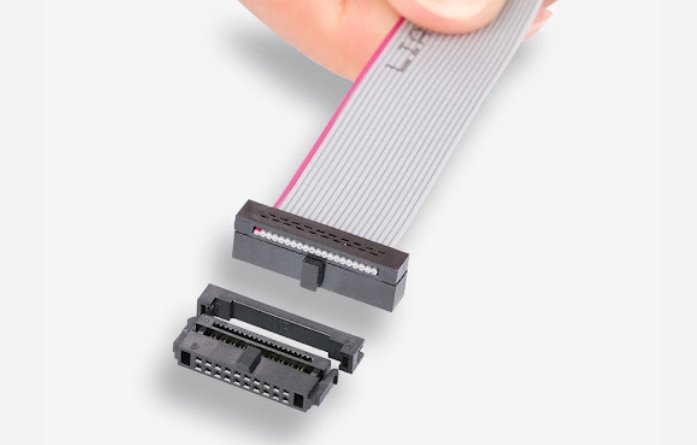

How Is the IDC Termination Process Carried Out Step by Step?
The IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) termination process is designed for speed, precision, and efficiency, particularly when working with flat ribbon cables. At Yihetai, we follow a strict and well-defined process to ensure every IDC assembly meets our high standards of electrical performance and mechanical reliability. Below is a detailed 6 step-by-step overview of how IDC termination is typically carried out:
Step 1: Prepare the Cable
Strip the outer jacket (sheath) of the cable carefully, exposing the individual insulated conductors. Only remove enough of the jacket to accommodate the IDC connector, while keeping the conductor pairs twisted as close to the termination point as possible to maintain signal integrity.
Step 2: Arrange and Organize Wires
Separate the individual wires or pairs and align them according to the wiring color code or pattern specified by the connector or industry standard (e.g., T568A or T568B for Ethernet cables). This ensures each conductor is correctly placed for termination.
Step 3: Insert Wires into IDC Connector
Place the arranged and aligned wires into the IDC connector’s slots or contacts. The IDC connector has precisely spaced slots designed to accept each conductor of the cable.
Step 4: Use a Press or Punch-Down Tool
Employ a punch-down tool or a mechanical press to force the cable wires firmly into the IDC connector. As the wires are pressed in, the sharp metal blades within the IDC connector pierce through the insulation and make direct contact with the conductor inside. The tool also trims off any excess wire protruding from the connector.
Step 5: Secure the Termination
Ensure the cable jacket is properly seated against the connector to provide strain relief and protect the termination site from mechanical stresses. Some connectors feature built-in strain relief clips or boots.
Step 6: Inspect and Test
Visually inspect the termination to check for correct wire placement, proper seating, and clean cuts. Perform electrical continuity and signal integrity tests to verify the quality of the termination.
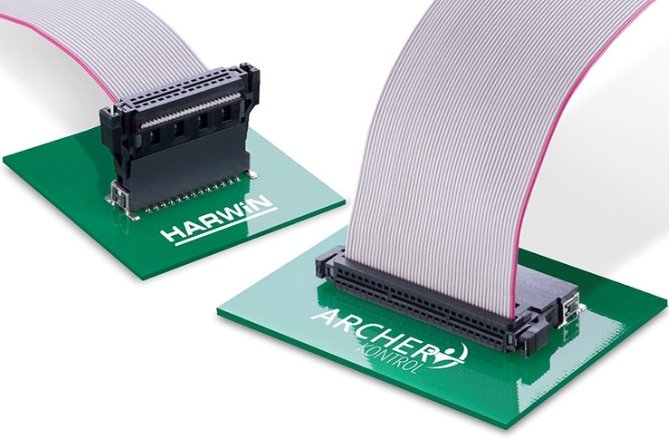
How Is Quality Assurance and Testing Conducted for IDC Cable Assemblies?
Quality assurance and testing are critical components in the production of IDC cable assemblies to ensure reliability, performance, and safety. The process involves multiple checks and tests designed to verify electrical integrity, mechanical strength, and overall assembly quality. Here is how quality assurance and testing are typically conducted for IDC cable assemblies:
1.Visual Inspection
Examine the cable assembly for proper cable routing, clean and undamaged connectors, correct wire color coding, and proper strain relief. This step helps catch obvious defects before functional testing.
2.Continuity Testing
This electrical test ensures that each conductor is correctly connected and there are no open circuits. A continuity tester or multimeter sends a small current through the wire to confirm uninterrupted flow.
3.Short Circuit Testing
Checks for unintended electrical connections between conductors that could cause shorts. The test identifies adjacent wires mistakenly touching or damaged insulation causing contact.
4.High Voltage (Hi-Pot) Testing
Also called dielectric strength testing, this applies a high voltage between conductors to verify insulation integrity. It ensures the cable can withstand operating voltages without current leakage or breakdown.
5.Resistance Measurement
Specialized milliohm meters measure the resistance within each conductor and contact interface. Higher than expected resistance can indicate poor connections like loose contacts or corrosion.
6.Pull and Flex Tests
Mechanical tests evaluate the robustness of the connectors and cable assembly under stress. Pull tests measure the force required to detach connectors or cause cable failure, while flex tests simulate repeated bending to verify durability.
7.Environmental Testing (Optional)
Depending on application, assemblies may undergo tests for temperature extremes, moisture resistance, and chemical exposure to ensure performance in harsh conditions.
8.Automated Testing Systems
Automated test equipment can simulate many of these electrical and mechanical tests, providing quick, consistent, and comprehensive quality verification. Some systems also feature guided assembly for error reduction during manufacturing.
How to Choosing the Right IDC Cable and Connector?
Choosing the right IDC cable and connector is essential to ensure a reliable, efficient, and durable connection for your specific application. Here are 7key considerations to guide you in selecting the appropriate IDC components:
1.Match Connector Pitch to Cable Pitch
IDC connectors and ribbon cables come in standard pitches, which refers to the spacing between conductors. Common pitches include 1.27mm (0.05 inch) for fine-pitch cables and 2.54mm (0.1 inch) for standard cables. Ensuring the connector pitch matches the cable conductor spacing is critical for proper termination and reliable contact.
2.Consider Wire Gauge Compatibility
IDC connectors are designed to accommodate specific wire gauges, usually expressed in AWG (American Wire Gauge) or mm². Verify that the connector supports the wire size of your cable to ensure secure insulation displacement and prevent damage or unreliable contacts.
3.Assess Current and Voltage Requirements
Based on your application, determine the electrical current and voltage the cable assembly needs to carry. Choose IDC connectors and cables that are rated for these specifications with an appropriate safety margin, considering factors like temperature rise and derating curves.
4.Environmental and Mechanical Considerations
Evaluate the operating environment temperature, humidity, vibration, and exposure to chemicals or mechanical stress. Some IDC connectors offer enhanced insulation materials, strain relief features, and robust housings suitable for harsh or industrial settings.
5.Connector Type and Application Needs
Select from available IDC connector types such as ribbon cable connectors, box headers, dual-row connectors, or application-specific variants depending on your wiring layout, number of conductors, and mating requirements (wire-to-board, wire-to-wire).
6.Assembly Method and Equipment Compatibility
Consider your termination process manual, semi-automatic, or automatic—and ensure the connector and cable are compatible with the available tooling. Proper tooling ensures consistent insertion force, contact reliability, and production efficiency.
7.Compliance and Standards
Ensure your IDC cable and connector selection conforms to industry standards (e.g., ROHS, CE) and any specific regulatory requirements related to safety, electromagnetic compatibility, or materials.
How Yihetai Supports IDC Cable Solutions
At Yihetai, we understand that IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) technology plays a vital role in modern cable assemblies, especially for high-density, compact, and signal-critical applications. With over 23 years of expertise in custom wire harness manufacturing, we provide full-service IDC cable solutions that combine precision engineering, advanced equipment, and industry-certified quality. Here’s how Yihetai stands out in delivering high-quality IDC cable assemblies:
1.Yihetai’s Experience with Flat and Ribbon Cable Assembly
Yihetai has extensive hands-on experience producing flat ribbon cable assemblies tailored to customer requirements across a wide range of industries. Whether for consumer electronics, industrial control systems, or automotive dashboards, our engineering team is skilled in handling multi-conductor configurations, compact layouts, and customized cable lengths. Our deep familiarity with IDC-compatible cable types ensures seamless integration and optimal performance.
2.In-House IDC Termination Capabilities
All IDC termination processes are performed in-house at Yihetai using specialized machinery and automated press tools. This allows us to control every step of production from precise cable cutting to connector insertion and pressing ensuring fast turnaround times and minimal error rates. Whether small batch or mass production, our facilities are equipped to handle high-volume IDC terminations with efficiency and consistency.
3.Quality Control and Certifications (ISO 9001, IATF16949, UL)
Quality assurance is at the core of every Yihetai product. All IDC assemblies undergo strict quality checks, including visual inspections, continuity testing, and mechanical pull-force verification. Our facilities are certified to ISO 9001:2015, IATF16949 (for automotive applications), and UL standards, giving our customers full confidence in product safety, reliability, and traceability. These certifications reflect our commitment to maintaining global manufacturing standards.
4.Custom Solutions for Various Industries
Yihetai specializes in providing custom IDC cable assemblies tailored to the needs of each industry. Whether it’s low-voltage data cables for medical devices, robust control cables for industrial automation, or ultra-flat IDC solutions for LED modules and smart appliances, we work closely with clients to design, prototype, and manufacture cables that meet specific functional and environmental demands. No matter the size, gauge, or configuration, we deliver purpose-built solutions with full technical support.
Conclusion
After exploring the basics of IDC cable termination, it is clear why this method is so widely used. Its ability to create fast, secure, and consistent connections makes it ideal for high volume production in industries ranging from consumer electronics to telecom and industrial control systems. The ease of assembly, reduced labor time, and dependable performance are advantages that cannot be overlooked.
When choosing the right termination method, I always recommend considering your production scale, cable type, and application requirements. IDC works best when you need efficiency without sacrificing quality, but it is important to match the connector style and materials to your specific project.
If you are looking for a trusted partner to provide reliable and customized IDC cable assemblies, I invite you to contact Yihetai. We can help you design, produce, and deliver solutions that meet both your technical and production needs with precision and care.


