Choosing the right cable for data transmission is never as simple as it seems. In industries such as automotive, telecommunications, medical equipment, or renewable energy, using the wrong type of cable can cause performance issues, signal interference, or even unexpected system failures. I have seen this happen many times with clients who were unsure which cable suited their needs best.
One of the most common questions I hear is, should I use coaxial cable or twisted pair cable? Both are popular, both are reliable, but they are built for different applications and environments.
That is exactly why I wrote this post. My goal is to help you clearly understand the differences between coaxial and twisted pair cables, and guide you in choosing the best option based on your specific application. Whether you are building new equipment, upgrading a communication system, or sourcing cables for your product, this article will give you the clarity you need.
What is a Coaxial Cable?
Before diving into a direct comparison, it is essential to understand what coaxial cables are. Once you see how they are built and where they are used, it will become easier to judge whether they are the right choice for your project.
Definition and structure
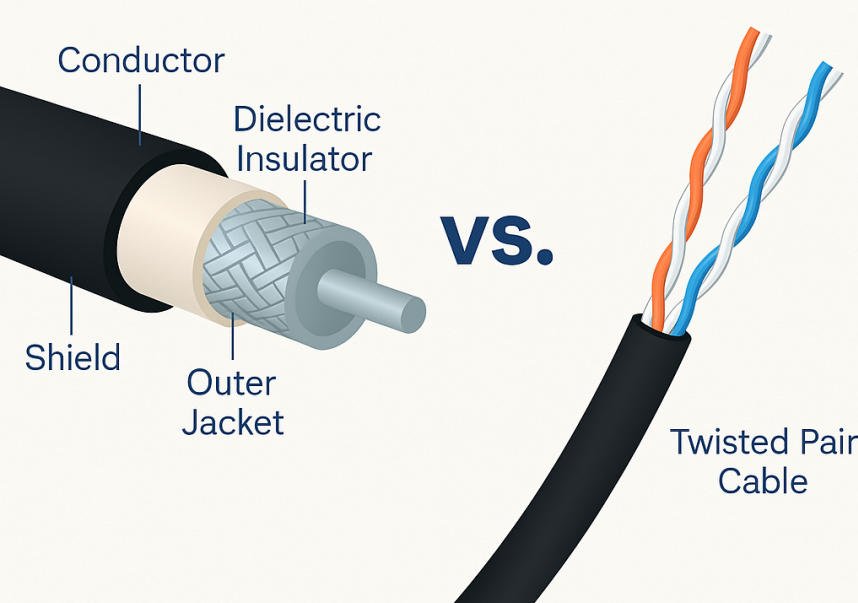
A coaxial cable (coax) consists of a central metal conductor, usually copper or copper‑clad steel, that carries the signal. Around this core sits a dielectric (insulating) layer, one or more metallic shields (foil and/or braided metal), and an outer plastic jacket that protects the cable mechanically and environmentally.
- Inner conductor: Solid or stranded copper/copper‑clad steel, responsible for transmitting RF or broadband signals.
- Dielectric insulator: Plastic such as polyethylene or similar materials that maintains a precise spacing between core and shield and sets the cable’s characteristic impedance (often 50 Ω or 75 Ω).
- Shield: One or more layers of metal braid and/or foil that confine the electromagnetic field and block external EMI.
- Outer jacket: PVC or other robust polymer providing abrasion, UV, and moisture protection for indoor or outdoor use.
How coaxial cable works
In a coaxial cable, the signal travels along the inner conductor while the return path flows on the inner surface of the outer shield, forming a controlled transmission line. The electromagnetic field is largely contained within the dielectric between core and shield, which both reduces radiation out of the cable and minimizes susceptibility to external noise.
Because the core and shield are coaxial, impedance remains nearly constant along the length of the cable, enabling efficient transmission of high‑frequency or broadband signals over relatively long distances. Properly terminated coax (with matching connectors and loads) keeps reflections low, preserving signal quality for applications like cable TV, DOCSIS internet, and RF links.
Common coaxial types
Coaxial cables are produced in many “RG” families that differ in impedance, diameter, dielectric, and shielding, which affects loss, bandwidth, and flexibility. For low‑loss RF and broadband distribution in homes and businesses, 75‑ohm RG‑series cables such as RG6, RG59, and RG11 are especially common.
- RG6 (75 Ω): Widely used for cable TV, satellite TV, and cable internet; thicker dielectric and better shielding than RG59, allowing longer runs and higher‑frequency operation.
- RG59 (75 Ω): Thinner, more flexible cable typically used for shorter analog video and CCTV runs where very high frequencies and long distances are not critical.
- RG11 (75 Ω): Larger‑diameter, lower‑loss cable suited to long trunk runs in CATV or broadband systems where signal must travel further before amplification.
- Other 50‑ohm coax families (such as LMR‑series, RG58, RG213, etc.) are widely used in RF, cellular, and radio communication, balancing power handling and attenuation for antenna feeds and wireless infrastructure.
Applications of Coaxial Cables
- CCTV and Surveillance Systems: For stable video signal transmission.
- Cable TV and Broadband Internet: Backbone of many home and office networks.
- RF and Antenna Systems: Used in broadcasting, radio communication, and GPS systems.
- Medical and Aerospace Equipment: In precision applications requiring shielded, high-frequency transmission.
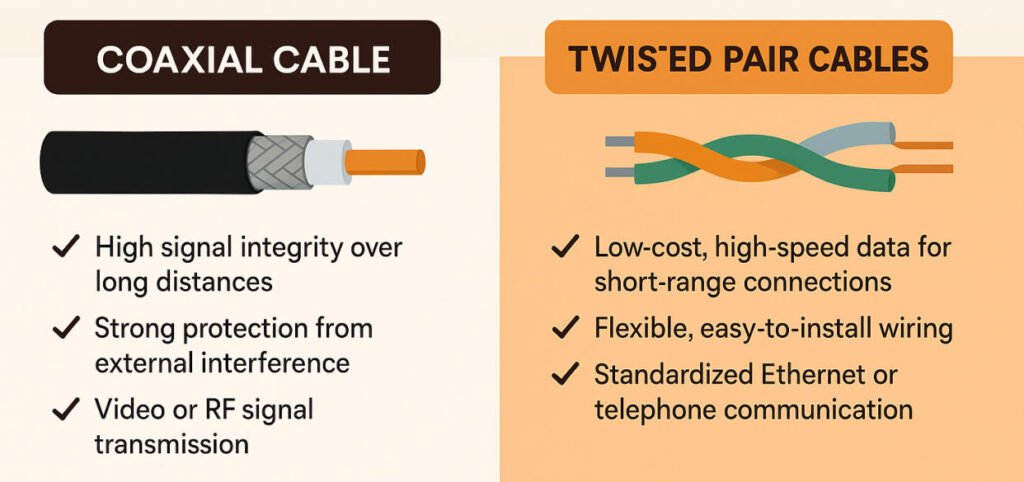
Pros and Cons of Coaxial Cables
To help you weigh your options quickly, here’s a clear comparison:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| EMI Resistance | Superior shielding (braided/foil layers) blocks interference effectively | Bulkier design from multiple layers increases physical size |
| Long-Distance Performance | Maintains signal integrity over extended runs with low attenuation | Higher material costs due to copper and shielding |
| Bandwidth | Supports high frequencies for video/data (e.g., HDTV, DOCSIS internet) | Less flexible for tight bends or high-speed LAN compared to twisted pair |
| Durability | Robust jacket withstands environmental damage | Heavier and harder to install in dense wiring setups |
What is a Twisted Pair Cable?
Now that we’ve explored coaxial cables, let’s take a look at their most common alternative: twisted pair cables. In my experience working across industries like telecom, industrial automation, and even automotive systems, twisted pair cables are often the go-to solution for many applications. They’re cost-effective, easy to install, and widely supported but they also have their limits. Here’s what you need to know.
What is a Twisted Pair Cable?
A twisted pair cable is made of two insulated copper wires twisted together, which helps reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) from external sources and from adjacent pairs. The twisting works by canceling out interference and crosstalk, making it a reliable and budget-friendly option for data and voice transmission.
What’s the Difference Between UTP and STP?
There are two main types of twisted pair cables, and choosing the right one depends on your environment:
UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
Most commonly used. No additional shielding. Ideal for offices, homes, and places with low EMI.
STP (Shielded Twisted Pair)
Includes a metal shield around the wire pairs for extra EMI protection. Best for industrial or high-interference environments.
Common Categories
Cat5e supports up to 1 Gbps at 100 MHz for basic Gigabit Ethernet. Cat6 handles 10 Gbps at 250 MHz with tighter twists and separators for reduced crosstalk. Cat7 uses S/FTP shielding for 10 Gbps+ at 600 MHz, suiting high-speed data centers.
Applications of Twisted Pair Cables
| Application | Description |
| Local Area Networks (LAN) | Widely used in Ethernet-based home and office networks. |
| VoIP and Telephone Lines | Common in digital and analog voice communication systems. |
| Automotive and Industrial Control Systems | Used in data transmission between sensors, controllers, and modules. |
Pros and Cons of Twisted Pair Cable
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Inexpensive materials and manufacturing | Limited shielding invites EMI in harsh environments |
| Flexibility | Thin, bendable for easy installation in walls/patches | Shorter max range (100m for Ethernet) vs. coax |
| Compatibility | Universal support in Ethernet/VoIP standards | Higher crosstalk/attenuation at very high frequencies |
| Installation | Lightweight and simple terminations | Vulnerable to bends damaging twists |
What Are The Differences Between Coaxial and Twisted Pair Cables
Now that we’ve looked at each cable type in detail, the next step is to compare them side by side. I often get asked, “Which one should I choose?” The answer always comes down to the specific needs of your application. While both coaxial and twisted pair cables are used for signal transmission, they are very different in terms of design, performance, and best-use scenarios.
Let me help you understand the key differences:
| Feature | Coaxial Cable | Twisted Pair Cable |
| Structure | Central conductor surrounded by dielectric, shielding, and outer jacket | Two insulated copper wires twisted together |
| Shielding | Strong shielding provides excellent protection against electromagnetic interference | UTP has no shielding, STP has moderate shielding |
| Signal Quality | Maintains high signal integrity over long distances | Performs well at short to medium distances, more affected by noise |
| Bandwidth | Ideal for high-frequency signals such as RF and video | Designed for high-speed data networks like Ethernet |
| Installation | Less flexible and thicker, better for fixed or industrial installations | Easy to install, lightweight and flexible |
| Cost | Higher material and installation cost | More affordable, widely used in commercial and residential networks |
| Typical Applications | Cable television, CCTV, satellite, antennas, medical systems | LAN, VoIP, telephone wiring, automotive and factory control systems |
From my experience, coaxial cables are best when you need strong shielding and long-range performance, especially in environments with lots of electrical noise. Twisted pair cables are a great fit for modern data networks, offices, and smart systems where flexibility and cost efficiency matter more.
Which Cable is Right for Your Application?
Now that we’ve compared coaxial and twisted pair cables in terms of structure, performance, and usage, the final question is simple but important: Which one should you actually use for your project?
From my experience working with different industries and applications, I know that choosing the right cable depends on more than just specs,it depends on real-world needs. Let me guide you through the best options based on your specific situation.
Use Coaxial Cable if you need:
- Reliable signal quality over long distances
- Strong shielding against electrical noise or interference
- Transmission of video, radio frequency (RF), or broadband signals
- Use in environments like CCTV setups, cable TV, or antennas
Coaxial cables are the go-to solution when signal integrity and shielding are top priorities
Use Twisted Pair Cable if you need:
- Budget-friendly, high-speed connections within short or medium distances
- Easy and fast installation with more flexibility in routing
- A cable that supports Ethernet, VoIP, or telephone systems
- Use in office networks, smart home wiring, or automotive systems
Twisted pair cables are ideal when cost, speed, and flexibility are more important than extreme shielding or long-distance performance.
If you’re still unsure which type is best for your setup, I’d be happy to help you evaluate your application. At Yihetai, we specialize in building custom wire harnesses tailored to your exact needs whether you choose coaxial, twisted pair, or a combination of both.

How to Choose the Right Cable for Your Project
By now, you understand the strengths of both coaxial and twisted pair cables. But when it comes to real-world projects, many people still ask me, “How do I know which one to choose?” To make that decision easier, I always recommend asking a few practical questions.
Let’s walk through them together:
Ask Yourself These Questions
Is your environment full of electrical noise or interference?
If yes, coaxial cable is usually the better choice due to its strong shielding.
Are you transmitting video, data, or both?
Coax is ideal for video and RF signals, while twisted pair is great for data and control communication.
How far does the signal need to travel?
Coaxial handles long distances better without signal loss. Twisted pair works well for short to medium distances.
Do you have limitations on size, weight, or budget?
Twisted pair is more compact, easier to install, and more cost-effective.
General Rule of Thumb
- Choose coaxial cable for applications involving RF signals, video transmission, or environments with high interference
- Choose twisted pair cable for data, control signals, telephone systems, or when flexible routing is required
Still not sure? I help customers every day figure out the best cable for their specific project. Whether it’s industrial automation, telecom systems, or automotive wiring, our team at Yihetai can provide custom cable assemblies that meet both your technical and budget needs.
Real Industry Use Cases For Coaxial Cable and Twisted Pair Cable
To truly understand the difference between coaxial and twisted pair cables, I always recommend looking at how they’re actually used in the field. These aren’t just theoretical specs they translate into real applications across a wide range of industries. I’ve worked with clients in sectors from aerospace to automation, and each project has its own technical demands. Here’s how these cables are used in the real world to solve real problems.
Coaxial Cable – Real-World Applications
| Industry | Use Case |
| Surveillance | Connects analog or HD CCTV cameras to DVRs for long-distance, high-quality video |
| Medical Equipment | Carries sensitive signals in diagnostic tools like ECG and ultrasound systems |
| RF & Broadcasting | Transmits high-frequency signals in radio stations, test benches, and antennas |
| Aerospace & Military | Used in precision sensors, radar systems, and avionics where EMI shielding is critical |
Twisted Pair Cable – Real-World Applications
| Industry | Use Case |
| Industrial Automation | Connects PLCs, sensors, and actuators in machinery and control systems |
| IT & Networking | Backbone of Ethernet LANs, internet access, and structured cabling |
| Smart Buildings | Powers smart lighting, access control, and climate systems via PoE & data |
| Automotive | Supports CAN bus communication between ECUs, sensors, and infotainment units |

When Off-the-Shelf Isn’t Enough – Go Custom
Sometimes, choosing between coaxial and twisted pair cables is only the first step. In many of the projects I support, standard cables just do not meet all the requirements. Maybe you need a specific cable length, a special type of insulation, or a connector that fits a unique device. This is when regular stock cables are no longer the right solution.
That is where Yihetai’s custom cable harness solutions make a real difference.
We provide complete support from early design and sample development to full-scale production. Every cable is built according to your exact technical and environmental requirements. Whether it is enhanced shielding, temperature resistance, or non-standard connectors, we can deliver a solution that fits your needs perfectly.
Our production is certified to ISO 9001, UL, and IATF16949, giving you peace of mind in both quality and performance. We proudly serve industries such as automotive, medical, industrial control, energy, telecommunications, and many more.
If your project requires more than what is available off the shelf, I would be glad to help you explore a custom solution that is built to last and ready to perform.
Why Choose Yihetai for Custom Cable Assemblies
After exploring the differences between coaxial and twisted pair cables, and understanding when a custom solution is needed, the next question becomes clear. Who can deliver a cable assembly that meets your exact requirements with consistency and quality? This is where I truly believe Yihetai is the right partner.
With more than 23 years of experience in wire harness manufacturing, we have supported customers across a wide range of industries. From coaxial cable assemblies to twisted pair wiring solutions, we provide complete support from concept to production.
All major processes are handled directly in our own facilities. This includes cable cutting, crimping, molding, bundling, assembly, and electrical testing. Because we manage everything in one place, we can ensure better quality control, faster turnaround, and greater flexibility for your project.
Yihetai holds certifications including ISO 9001 2015, UL, and IATF 16949, which reflect our commitment to international quality standards.
We proudly serve industries such as automotive electronics, industrial control, medical equipment, renewable energy systems, and more. Whatever your application, we have the tools, the people, and the experience to deliver exactly what you need.
If you are ready to move forward with a reliable and efficient custom cable solution, I would be glad to support you at every step.
Conclusion
At the end of the day, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to coaxial vs. twisted pair cables. Your choice will directly affect your system’s speed, signal quality, durability, and even your overall cost. That’s why it’s so important to choose carefully.
My advice? Always consider the transmission distance, the level of electromagnetic interference (EMI) in your environment, your specific application, and the working conditions the cable will face. These factors will point you toward the right solution for your project.
Still not sure which cable is the best fit? Don’t worry – we’re here to help. At Yihetai, we specialize in custom wire harnesses that are tailor-made for your exact needs. Whether you need better shielding, faster data transmission, or long-lasting durability, we’ll work with you to build the perfect solution.


