Choosing the right coaxial cable might seem like a small detail, but it can have a big impact on signal quality, system reliability, and long-term performance. I have seen many people underestimate this decision, only to face poor video clarity or unstable connections later. That is why understanding your options is so important before starting any installation.
Two of the most commonly used coaxial cables are RG6 and RG59. Both are widely used in residential and commercial settings, including satellite television, security systems, and video transmission. While they may look similar on the outside, they perform very differently depending on the application.
In this blog, I will walk you through the key differences between RG6 and RG59, explain where each one works best, and help you decide which cable is the right fit for your project. Let’s take the guesswork out of your decision and find the best solution for your needs.
What Is RG6 Coaxial Cable?
To make the right choice between RG6 and RG59, it’s important to understand what each cable is designed to do. While they may look similar on the outside, their construction and performance are quite different. Let me start by breaking down what RG6 coaxial cable is, and where it truly shines.
What Is RG6 Coaxial Cable?
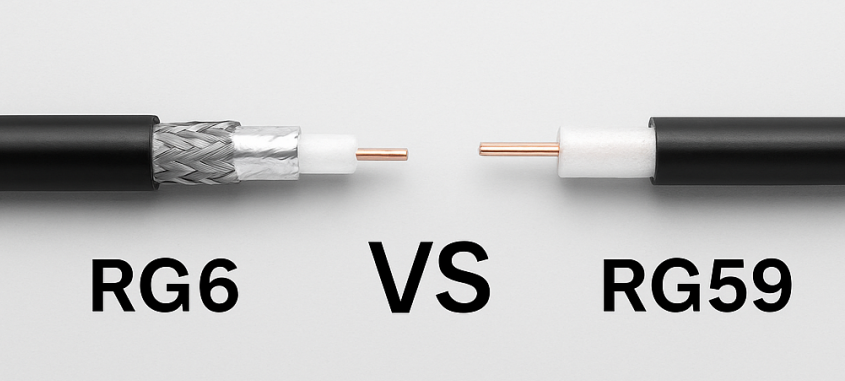
RG6 is a 75-ohm coaxial cable that’s widely used in modern TV, satellite, and internet installations. It features a thicker center conductor, usually 18 AWG, and a larger dielectric insulator compared to RG59. This design helps minimize signal loss, especially over longer distances.
One of RG6’s key strengths is its superior shielding—typically a combination of aluminum foil and braided shielding, and in many cases, double or quad-shielded. This makes it excellent for environments with high electromagnetic interference or when the cable needs to run near power lines or other signal sources.
Thanks to its low signal attenuation and high-frequency support, RG6 performs exceptionally well in applications such as:
- Cable TV and satellite TV installations
- DOCSIS broadband internet connections
- Longer in-wall or outdoor runs
If you’re working with high-bandwidth signals or need reliability over distance, RG6 is often the better choice. It’s built to handle today’s digital signals with clarity and consistency, even in demanding conditions.
What Is RG59 Coaxial Cable?
Now that we’ve looked at RG6, let’s take a closer look at RG59 the other common coaxial cable that’s still widely used today. While it may not match RG6 in terms of performance over long distances or high frequencies, RG59 has its own advantages, especially in specific use cases where flexibility and lower frequencies are the priority.
What Is RG59 Coaxial Cable?
RG59 is also a 75-ohm coaxial cable, but it’s built differently from RG6. It typically has a smaller center conductor, around 20 to 22 AWG, and a thinner dielectric layer. Because of this lighter construction, RG59 is generally more flexible and easier to work with in tight or compact spaces.
Shielding is usually more basic a single layer of braided copper which offers less protection against interference compared to RG6. This limits RG59’s effectiveness in high-frequency or high-interference environments.
When it comes to performance, RG59 tends to lose signal more quickly at higher frequencies, so it’s best suited for low-frequency applications and short to medium cable runs.
Typical applications include:
- Analog CCTV surveillance systems
- Short patch cables in AV setups
- Baseband video and audio distribution
- Legacy or retrofit installations where RG59 is already in use
If your project involves older video systems, or you simply need a cost-effective solution for short runs, RG59 can still be a solid choice. It delivers reliable performance within its limits and remains popular in security and AV environments where ultra-high bandwidth isn’t required.

Waht Are Key Differences Between RG6 Coaxial Cable and RG59 Coaxial Cable?
Once you understand the basics of RG6 and RG59, the next step is to compare them side by side. Both are 75-ohm coaxial cables, but their physical construction and performance capabilities make them suitable for different types of installations. To help you decide which one fits your needs, I’ve put together a quick comparison of their most important differences.
| Feature | RG6 Coaxial Cable | RG59 Coaxial Cable |
| Conductor Size | Thicker (typically 18 AWG) | Thinner (typically 20–22 AWG) |
| Shielding | Better shielding (foil + braid, often double or quad) | Basic shielding (usually single braided) |
| Frequency Support | Supports higher frequencies, ideal for digital signals | Limited to lower frequencies, better for analog signals |
| Signal Range | Lower loss over long distances | Higher loss, best for short to medium runs |
| Flexibility | More rigid due to thicker build | More flexible, easier to install in tight spaces |
| Price | Slightly more expensive | Generally more affordable |
When Should You Choose RG6 Coaxial Cable?
After comparing the key differences between RG6 and RG59, the next question I often hear is: “When exactly should I use RG6?” The answer depends on your specific application and performance requirements. Let me walk you through the situations where RG6 is clearly the better choice.
When Should You Choose RG6 Coaxial Cable?
1.Satellite TV and HDTV Installations
If you’re setting up satellite television or high-definition TV services, RG6 is the way to go. Its ability to handle higher frequencies and reduce signal loss means you get a sharper, more reliable picture without interference.
2.Cable Internet (Broadband Connections)
For internet connections using DOCSIS technology, such as cable modems, RG6 ensures your data travels efficiently with minimal loss. It supports the bandwidth and stability needed for modern, high-speed internet access.
3.Longer Cable Runs
When the installation requires cables to run over long distances—whether across a building or through multiple roomsRG6 performs far better than RG59. Its thicker core and enhanced shielding help preserve signal quality from end to end.
4.Outdoor and Harsh Environment Use
RG6 is built tough. Many versions come with UV-resistant jackets and waterproofing, making them suitable for outdoor installations, wall feeds, or industrial areas where exposure to the elements is a concern.
If your setup demands durability, high-frequency performance, and long-distance reliability, RG6 is the clear winner. I always recommend it for demanding applications where signal quality simply can’t be compromised.
When Should You Choose RG59 Coaxial Cable?
While RG6 is well suited for high-frequency and long-distance needs, there are still many situations where RG59 is actually the better choice. I often recommend RG59 for projects where the signal requirements are lower and the installation conditions are more compact or cost-sensitive. Let me explain where RG59 really performs best.
When Should You Choose RG59 Coaxial Cable
1.Analog CCTV Camera Systems
For traditional analog security systems, RG59 remains a dependable option. It is designed to carry low-frequency baseband video signals, which makes it ideal for older CCTV setups that do not require high-speed data transfer.
2.Shorter Distance Runs
If your installation involves short cable runs within a room or between nearby equipment, RG59 handles the job with no problem. Signal loss is minimal over short distances, and it provides a clean and simple solution.
3.Tight Spaces or Indoor Installations
RG59 is thinner and more flexible compared to RG6, which makes it easier to route through narrow spaces, behind walls, or in crowded AV racks. When space is limited, this flexibility can make installation quicker and cleaner.
4.Lower-Cost, Low-Frequency Applications
If your application does not require high definition video or high-frequency data transmission, RG59 offers excellent value. It is a cost-effective solution for audio, baseband video, or legacy AV equipment where performance demands are modest.
In summary, if you are working on a shorter run, dealing with analog signals, or simply need a flexible and budget-friendly option, RG59 can be the perfect fit. I always say the right cable is the one that meets your actual needs, not just the one with the highest specs.

Are RG6 and RG59 Interchangeable?
No, RG6 and RG59 coaxial cables are not truly interchangeable, despite sharing the same 75 Ω impedance and F-type connector compatibility using the wrong one for your application can lead to signal degradation, dropouts, or outright failure over distance or at higher frequencies.
While both cables can physically connect to the same ports and work for very short runs under ideal conditions, their core differences in construction make them unsuitable substitutes in most real-world scenarios. RG6’s thicker 18 AWG conductor, foam PE dielectric, and dual foil-plus-braid shielding (often quad) deliver far lower attenuation and better EMI rejection, allowing reliable performance up to 3 GHz over 100+ feet. In contrast, RG59’s thinner 20-22 AWG conductor and simpler braided shield result in higher signal loss (e.g., 12 dB/100 ft at 1 GHz vs. RG6’s 7 dB) and weaker high-frequency handling, limiting it to below 50-100 MHz and shorter distances.
Physically, the size mismatch creates practical issues too: RG6 requires larger compression or crimp F-connectors that won’t properly grip RG59’s thinner jacket and dielectric, risking poor terminations, water ingress, or intermittent connections. Attempting to force RG59 connectors onto RG6 often leaves the cable under-clamped, leading to signal leaks or mechanical failure many installers report this as a common “DIY disaster” that causes pixelation in TV signals or slow internet.
Performance-wise, swapping them predictably backfires based on use case. RG59 in a long RG6-optimized run (e.g., cable TV or broadband modem over 50 feet) suffers excessive loss, especially above 500 MHz, causing weak signals, data errors, or the need for costly amplifiers. Conversely, RG6 works fine in RG59’s short, low-frequency niches like basic CCTV, but its stiffness makes it harder to route in tight spaces, and it’s overkill (and more expensive) for those jobs.
Tips for Installation Considerations
After choosing between RG6 and RG59, the next step is making sure your installation is done correctly. I have found that even the best cable can perform poorly if installed with the wrong connectors or placed in the wrong environment. Here are some key factors I always consider during coaxial cable installation.
Flexibility and handling
RG59 is thinner and more flexible, which makes it easier to route through tight spaces, around corners, or behind walls. It is a great option when space is limited or when cables need to bend sharply. RG6, on the other hand, is thicker and stiffer. While that makes it slightly harder to work with, it offers better durability and is more reliable for longer cable runs or outdoor installations.
Connectors and tooling
Both RG6 and RG59 use common connectors like F-type and BNC, but it is important to use the correct size. RG6 requires connectors that fit its thicker core and insulation, while RG59 connectors are made for its smaller diameter. Using mismatched connectors can lead to poor signal contact or physical damage. Whether you are crimping or using compression connectors, always choose tools and parts designed for the exact cable type you are installing.
Jacket types and environments
The outer jacket of a coaxial cable should match the environment where it will be installed. For indoor use, a standard PVC jacket may be enough. For outdoor setups, look for cables with UV-resistant jackets to protect against sunlight. In buildings where fire codes apply, you might need plenum-rated or low smoke zero halogen (LSZH) jackets. These materials are designed to reduce toxic smoke and comply with safety regulations.
By paying attention to these details during installation, you will get the best performance from your coaxial cable, no matter which type you choose. Proper handling, the right connectors, and the correct jacket can make all the difference in long-term reliability.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Over the years, I have seen many installations fail to perform simply because of a few easily avoidable mistakes. Choosing between RG6 and RG59 is not just about understanding the specs, but also knowing how and where to apply them. Let me walk you through some of the most common errors and how to prevent them.
Using RG59 for Long High Frequency Runs
One mistake I often see is using RG59 in systems that demand high bandwidth over distance, such as cable television or broadband internet. RG59 is not built for this type of signal load, and you may end up with blurry video, slow data speeds, or constant dropouts. If your setup involves high frequency transmission or long cable runs, RG6 is the right choice.
Mixing Cable Types or Reusing Old RG59
It may be tempting to reuse older cables or combine different types in one system, but this usually leads to poor signal quality and inconsistent results. I always recommend choosing one cable type for the entire run and avoiding old RG59 when upgrading to modern digital services. Even if the connectors fit, the performance will not match.
Ignoring Printed Markings and Technical Specs
Another mistake is ignoring the printed information on the cable jacket. These markings tell you key details like the frequency rating, shielding type, and whether the cable is rated for outdoor or in-wall use. I always check this information before installation to ensure the cable meets both performance and safety requirements.

Industry Insights: What We See in 2026 for RG6 and RG59 Coaxial Cable
In 2026, RG6 solidifies its dominance as the go-to coaxial cable for high-bandwidth residential and commercial installs, while RG59 carves a shrinking but persistent niche in legacy and short-haul analog systemsreflecting broader trends toward hybrid networks and cost-conscious upgrades.
RG6 demand surges with ongoing HFC (hybrid fiber-coax) network expansions by cable providers, pushing multi-gig internet to rural areas and aging urban plants through 2026. Enhanced quad-shield variants with lower-loss foam dielectrics support DOCSIS 4.0 and 8K video, making RG6 essential for new drops, in-home splits, and outdoor antenna feeds where signal integrity over 100+ feet is non-negotiable. Manufacturers report 15-20% YoY growth in plenum-rated and direct-burial RG6, driven by smart home retrofits and 5G small-cell backhaul.
RG59, meanwhile, persists in budget CCTV upgrades using HD-over-coax tech (like HD-TVI/AHD) for short camera runs under 100 feet, where its flexibility shines in tight conduits or legacy buildings. However, it’s fading from new TV/internet projects due to high attenuation above 700 MHz installers increasingly swap it out during service calls, favoring RG6 to eliminate pixelation complaints. Expect RG59 volumes to plateau or decline 5-10%, confined to low-voltage AV, baseband video, and repair stockpiles.
Key 2026 shifts include greener materials (recycled PE jackets, lead-free solders) across both types to meet EU RoHS updates, plus pre-terminated assemblies with weatherproof boots for faster DIY and pro installs. RG6 benefits most from these, positioning it as the future-proof choice, while RG59 survives as a “good enough” option for non-critical, short-distance analog holdouts.
Looking ahead, I believe RG6 will continue to take the lead, especially as demand for high-definition content and stable broadband increases. But RG59 will still have a place where simplicity, flexibility, and lower costs are priorities. The key is knowing when and where to use each one.
Yihetai’s Custom Coaxial Cable Solutions
At Yihetai, we specialize in manufacturing custom coaxial cable assemblies, including both RG6 and RG59 types. Every solution is designed to meet the technical and environmental needs of your application, whether for a small batch or large-scale production.
We offer full customization options, including:
- Specific cable lengths tailored to your installation
- Connector types such as F-type, BNC, or custom interfaces
- Overmolding for added protection and durability
- Labeling and color coding for easy identification
- OEM and ODM batch production based on your project demands
Our coaxial cable solutions are used in various industries including:
- Security and surveillance systems
- Broadcast and video distribution
- Automotive electronics
- Telecommunications and infrastructure projects
Every product is 100 percent tested and certified, with compliance to UL standards, ISO 9001, and IATF 16949. This ensures consistent quality, safety, and traceability for every cable assembly we deliver.
If your project requires dependable performance and professional support, I encourage you to connect with us. At Yihetai, we make sure your coaxial cable solution is not just functional, but optimized for long-term success.
Conclusion
Now that we have looked closely at the differences between RG6 and RG59, the choice should feel much clearer. RG6 offers better shielding and supports higher frequencies, making it ideal for long-distance runs, high-definition video, and satellite or internet signals. On the other hand, RG59 is more flexible and cost-effective for short-distance applications, especially in analog CCTV systems or indoor setups.
When I help customers choose the right coaxial cable, I always suggest focusing on three things: frequency requirements, cable length, and installation environment. These factors will guide you to the right solution that balances performance and budget.
At Yihetai, we provide custom coaxial cable assemblies tailored to your project, whether you need RG6, RG59, or something more specialized. If you are unsure which one fits your needs best, I am here to help you make the right decision with confidence.


