Have you ever seen the “Check Engine” light come on and wondered what is really happening inside your vehicle? That is where OBD, short for On Board Diagnostics, becomes important. It is a built-in system found in modern cars that monitors the engine, emission systems, and other key components. When something goes wrong, OBD helps identify the issue early.
But here is the challenge. Without the proper connection to this system, you cannot access the information your vehicle is trying to share. That is why the OBD cable is so valuable. It acts as the bridge between your car’s computer and your diagnostic tool, allowing you to read error codes, view live data, and make informed repair decisions.
In this blog, I will explain what an OBD cable is, how it works, and why it matters. If you want reliable, accurate diagnostics, understanding this cable is the first step.
What Is On-Board Diagnostics (OBD)?
Before we dive into how an OBD cable works, it’s important to first understand exactly what it is and why it matters. If you’ve ever plugged a scan tool into your vehicle to check a warning light or monitor performance data, you’ve already used one even if you didn’t realize it. Let me explain in simple terms what an OBD cable does and how it fits into the vehicle diagnostics process.
What Is an OBD Cable?
An OBD cable, short for On-Board Diagnostics cable, is a specialized communication link that connects your vehicle’s onboard computer system to an external diagnostic tool, such as a scanner, laptop, or mobile interface. It allows the transfer of critical data, including fault codes, sensor readings, and engine performance information.
The main function of the OBD cable is to enable real-time communication between the vehicle and the technician or user, making it easier to detect issues, reset warning lights, and even perform repairs with confidence.
There are two main types of OBD cables:
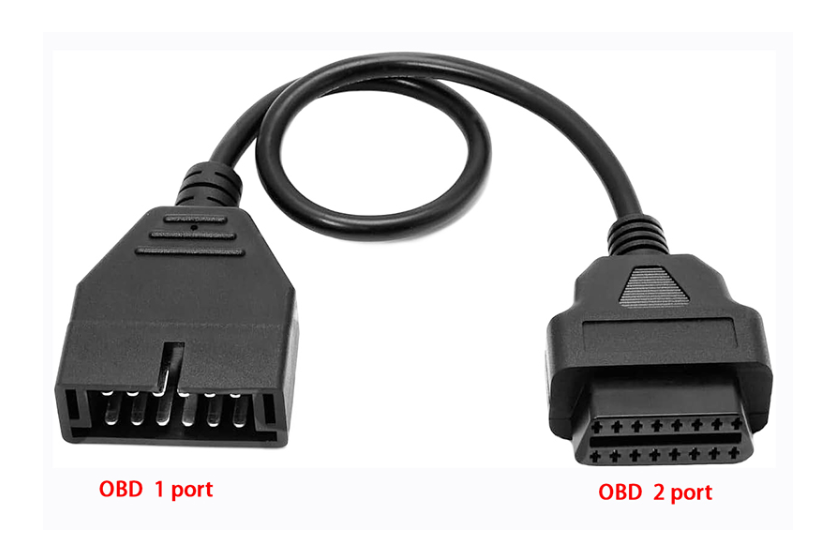
- OBD1 cables were used before 1996 and are usually manufacturer-specific. Each brand had its own connector shape and pin layout, which often required a matching scanner.
- OBD2 cables, introduced in 1996, follow a universal 16-pin standard and are compatible with most modern vehicles. They offer broader data access and support a variety of communication protocols.

How Does an OBD Cable Work?
Now that we’ve covered what an OBD cable is and what the OBD system does, let’s dive into the most important part, how the cable actually works. Whether you’re using it for basic diagnostics or advanced ECU scanning, the OBD cable plays a key role in transferring critical information from your vehicle to your diagnostic tool. Here’s how the process works step by step.
How Does an OBD Cable Work?
Physical Connection to the Vehicle’s Diagnostic Port
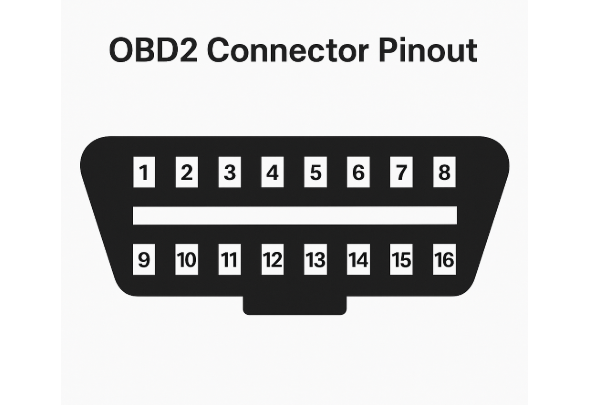
An OBD cable plugs directly into the vehicle’s diagnostic port, usually located beneath the dashboard on the driver’s side. In vehicles equipped with OBD2, this port uses a standard 16 pin trapezoidal connector. Once connected, the other end of the cable attaches to a diagnostic device, such as a scanner, laptop, or mobile application through a USB or Bluetooth adapter.
Data Transmission Between ECU and Scanner
Inside the vehicle, the Engine Control Unit (ECU) collects information from multiple sensors and control systems. When an OBD cable is connected, it creates a data path between the ECU and the diagnostic tool. The scanner sends requests for information, and the ECU responds with stored fault codes, sensor data, and system statuses. This enables accurate diagnostics and real time monitoring of vehicle performance.
Pin Layout and Communication Protocols
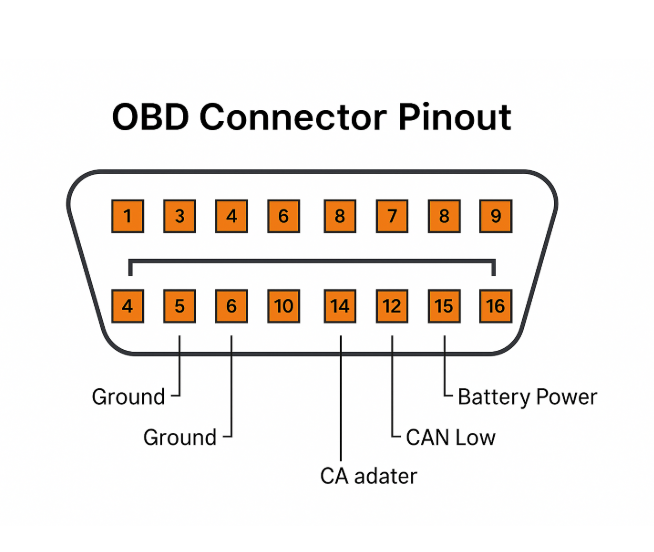
The OBD2 connector includes 16 pins, though the exact pin usage can vary depending on the vehicle. Key pins include:
- Pin 4 and Pin 5 for grounding
- Pin 16 for battery power supply
- Pin 6 and Pin 14 for CAN communication
- Pin 7 for ISO protocols used by many Asian and European vehicles
Communication between the vehicle and the diagnostic tool is managed through standardized protocols such as:
- CAN (Controller Area Network)
- ISO 9141
- SAE J1850
- KWP2000
Understanding the correct pin layout and protocol is essential to ensure a successful connection and accurate data reading.
Example: How a Mechanic Uses an OBD2 Cable
Imagine a technician working on a 2018 Toyota Corolla with the check engine light on. The mechanic connects an OBD2 cable to the diagnostic port and links it to a scanning device. Within seconds, the scanner retrieves a code, such as P0171, which indicates a lean fuel condition.
Using the same cable, the technician accesses live data from oxygen sensors and fuel trim levels. This detailed information helps pinpoint the cause quickly, avoiding unnecessary part replacement and reducing repair time.
The OBD cable is the bridge between your vehicle’s brain and the tools that help keep it running at its best. Without it, effective diagnostics would not be possible.

What Are The Types of OBD Cables
Now that we know how an OBD cable works, it is time to look at the different types available. Not all OBD cables are the same, and the right one depends on your vehicle, your diagnostic tool, and how you plan to use it. From older cars to modern vehicles, and from wired connections to wireless solutions, here is a breakdown of the most common OBD cable types and how they are used.
What Are the Types of OBD Cables?
OBD1 Cables
OBD1 cables are designed for vehicles manufactured before 1996. These systems were not standardized, so every manufacturer created its own connector style and protocol. As a result, OBD1 cables come in many different shapes, pin layouts, and sizes.
Example:
A Honda from the early 1990s may use a 3-pin connector, while a General Motors vehicle from the same period might use a 12-pin ALDL connector. Because of this variation, OBD1 cables must match the specific brand and model of the vehicle.
OBD2 Cables
In 1996, the industry introduced OBD2 as a standardized system. All OBD2 cables use the same 16-pin trapezoidal connector, making them compatible with most vehicles made after 1996. This universal design simplifies diagnostics and allows for greater compatibility between different vehicles and scan tools.
OBD2 cables support multiple communication protocols, including:
- CAN (Controller Area Network)
- ISO 9141
- SAE J1850
- KWP2000
Because of this, a single OBD2 cable can work across many makes and models, as long as the protocol is supported.

Wired vs. Wireless OBD Connectors
Wired OBD Cables
These provide a stable and direct connection between the vehicle and the diagnostic tool. They are commonly used in professional settings where reliability is essential.
Wireless OBD Adapters
These include Bluetooth, USB, or serial interface options. They plug into the OBD port and connect to a phone, tablet, or laptop wirelessly. While convenient, some wireless adapters may offer limited functionality compared to wired tools.
Example:
A car owner might use a Bluetooth OBD2 adapter with a smartphone app for basic code reading, while a technician performing deep diagnostics would rely on a wired OBD2 cable connected to a professional-grade scanner.
Custom vs. Universal OBD Cables
Universal OBD Cables
These are designed to work with most OBD2 vehicles and tools. They are ideal for general-purpose use and often come with basic features.
Custom OBD Cables
These are made for specialized applications, such as OEM diagnostic equipment, fleet tracking devices, or emissions testing tools. Custom cables may include unique pin configurations, specific lengths, molded connectors, or protective materials for harsh environments.
Example:
A fleet management company might request a custom OBD2 Y-cable that allows both a telematics device and a scanner to connect at the same time without interference.
What Are The Components Of An OBD Cable?
To understand how an OBD cable works and why quality matters, it helps to look inside. An OBD cable might look simple from the outside, but it’s made of several key components that work together to ensure reliable communication between your vehicle and diagnostic tool. In my experience, paying attention to these details is what separates a high-performing cable from one that fails when you need it most.
Connector Types: OBD1 vs OBD2
The most visible part of any OBD cable is the connector.
- OBD1 connectors vary widely by manufacturer. Some use rectangular, round, or multi-pin designs, and the location and pin layout differ from brand to brand. These connectors are typically used for older vehicles manufactured before 1996.
- OBD2 connectors follow a universal standard with a 16 pin trapezoidal shape. This design ensures compatibility with almost all vehicles built from 1996 onward, making it easier for workshops and car owners to diagnose issues using a single tool and cable.
Internal Wiring and Pin Configuration
Inside the cable, precision is key. Each pin in the connector corresponds to a specific function such as power, ground, or communication lines.
- Pin layout depends on the protocol being used, such as CAN, ISO, or J1850.
- OBD2 cables may use only a few active pins or all 16, depending on diagnostic requirements.
- A high-quality OBD cable features well-organized internal wiring with proper soldering, crimping, or ultrasonic welding to ensure strong signal transmission.
- Accurate wiring ensures that data moves smoothly between the vehicle’s control unit and the scanner without signal loss or electrical interference.
Material Quality: Shielding, Insulation, and Overmolding
The durability and performance of an OBD cable depend heavily on the materials used:
- Shielding protects the signal from outside interference, which is especially important in busy workshops where many electronic devices are in use.
- Insulation prevents short circuits and protects against heat, oil, and moisture. Common materials include PVC, TPE, and silicone rubber.
- Overmolding adds strength around the connector, providing protection against bending, pulling, or dust and moisture entering the cable housing. This also extends the lifespan of the cable under repeated use.
Each of these components plays a critical role in the performance and reliability of an OBD cable. Choosing cables built with quality materials and careful construction helps ensure consistent performance whether you are working in a professional garage or diagnosing a car at home.
Why OBD Cables Quality and Compatibility Matter
It can be easy to underestimate the importance of choosing the right OBD cable, especially when the focus is usually on the diagnostic tool or the vehicle itself. However, in my experience, the quality and compatibility of the cable often determine whether your diagnostic process is smooth and reliable or full of frustration and false readings. Let me explain why this matters more than most people think.
Why OBD Cable Quality and Compatibility Matter
1.Durability and Proper Shielding Ensure Long-Term Performance
A high-quality OBD cable is built to handle tough environments. It should have strong insulation to protect against heat, abrasion, and vibration. Shielding inside the cable is also important because it prevents outside electrical interference from affecting the signal. The outer layer should be well protected and firmly molded around the connector to handle repeated use without breaking down.
2.Poor-Quality or Incompatible Cables Create Real Risks
Using a cable that is not made for your specific tool or vehicle can lead to poor connections, incomplete data, or failure to communicate with the car’s computer system. I have seen cases where mismatched pin layouts or cheap materials caused the scan tool to freeze or deliver inaccurate codes. In some situations, a low-grade cable can even cause harm to sensitive vehicle electronics.
3.Custom Cable Solutions Meet Industry-Specific Needs
Some industries require more than a basic OBD cable. For example, automotive repair shops, vehicle testing centers, and fleet service companies often need cables designed for long hours of daily use. These cables must match advanced tools and custom diagnostic systems. This is where a trusted cable manufacturer like Yihetai makes a difference. They offer custom-built OBD cable solutions tailored to meet the technical and environmental needs of your application.
What Are The Real-World Applications Of OBD Cables?
Now that we know what OBD cables are and how they function, it is time to look at where they are used in real life. Whether you are a professional mechanic, a fleet manager, or just someone who likes working on cars, OBD cables serve as a critical tool in many automotive settings. Below are some of the most common and practical ways OBD cables are used today.
1.Vehicle Diagnostics in Workshops
One of the most common uses of OBD cables is in professional auto repair shops. Mechanics use these cables to connect diagnostic tools to the vehicle’s onboard computer system. This helps them:
- Read and clear fault codes
- Monitor live engine data
- Perform system resets and sensor checks
For example, a technician may use an OBD2 cable to diagnose a misfire by checking real-time data from each cylinder. This speeds up the repair process and ensures accurate troubleshooting.
2.Emissions Testing
Government regulations in many countries require emissions testing for vehicles. OBD cables are used to connect testing equipment to the car’s ECU to read emissions-related data.
- This includes oxygen sensor readings, fuel mixture, and catalytic converter efficiency
- The cable helps verify whether a vehicle meets environmental standards without taking apart the engine
- In some regions, a vehicle cannot pass inspection without a successful OBD check
OBD2 cables are especially important in modern emissions testing due to their standardized connector and supported protocols.
3.Fleet Management and Telematics
In the logistics and transportation industries, OBD cables are often part of larger telematics systems. These systems monitor:
- Vehicle health
- Driving behavior
- Fuel efficiency
- GPS location
Fleet managers use this data to schedule maintenance, reduce downtime, and improve safety. A durable, custom OBD cable helps ensure stable data transmission across hundreds of vehicles.
4.DIY Car Repair and Performance Monitoring
OBD cables are also popular among car enthusiasts and DIY mechanics.
- With a basic scanner or a mobile app, users can read trouble codes and reset check engine lights at home
- Performance tuners use OBD cables to track data like air-fuel ratio, RPM, and throttle response
- Some hobbyists even log real-time data to improve fuel efficiency or plan upgrades
Whether you are trying to fix a minor issue or monitor your vehicle’s behavior on a long road trip, a reliable OBD cable gives you access to valuable insights.
Why Choose Yihetai for OBD Cable Solutions
If you’re looking for reliable and high-quality OBD cable solutions, choosing the right manufacturing partner is just as important as choosing the right cable. Over the years, I’ve seen how a dependable supplier can make all the difference in performance, safety, and long-term cost. That’s why I always recommend working with an experienced and trusted company like Yihetai. Here’s what makes them a preferred choice for OBD cable solutions.
Why Choose Yihetai for OBD Cable Solutions
Proven Experience in OBD1 and OBD2 Cable Manufacturing
Yihetai has been designing and producing OBD cables for over two decades. With deep expertise in both OBD1 and OBD2 standards, they understand the technical requirements of older vehicles as well as modern diagnostic systems. Whether you need a standard OBD2 cable or a custom-built connector for a unique diagnostic setup, Yihetai has the experience to deliver it with precision.
Support for OEMs, Fleets, and Diagnostic Tool Companies
Yihetai works closely with clients across various industries. They support automotive manufacturers, fleet operators, emissions testing services, and diagnostic tool companies. From small batches to large-scale production, they offer flexible solutions tailored to the specific needs of each project.
Certified Quality You Can Rely On
All Yihetai products are built in compliance with strict international standards. Their manufacturing process is certified under ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and UL, ensuring full traceability, quality control, and product reliability. These certifications give clients confidence that every cable meets both technical and safety requirements.
Tailored Designs with Complete Testing and Pin Matching
Yihetai offers full customization, including connector molding, cable length, pin configuration, and labeling. Every cable goes through 100 percent testing to ensure correct pin mapping, signal integrity, and stable electrical performance. This attention to detail is especially important for advanced diagnostics, ECU programming, and specialized communication tools.
For any business or technician looking for dependable OBD cables that meet exact needs, Yihetai is a trusted partner that combines experience, precision, and certified quality in every product.
Conclusion
Now that you’ve made it to the end, let’s quickly recap. An OBD cable is the critical link between your vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system and your scan tool. It allows you to read trouble codes, monitor real-time data, and perform advanced functions like emissions testing or ECU communication. Whether you’re using a basic reader or a professional-grade diagnostic tool, the cable you choose plays a direct role in how well that connection works.
From my experience, choosing the right OBD cable depends on your vehicle type, diagnostic setup, and how you plan to use it. The right cable makes diagnostics smoother, more accurate, and a lot less frustrating.
If you’re looking for a custom OBD cable for your workshop, product, or business, I recommend working with a reliable manufacturer like Yihetai. Their experience, precision, and certified quality make them a great partner for professional and tailored cable solutions. Feel free to reach out with any questions.


