If you are working with compact electronics, you have probably struggled to make all the internal components fit within limited space. Ribbon cables, with their flat and flexible structure, are commonly used in devices like laptops, medical tools, and consumer electronics because they allow multiple conductors to run side by side in an organized way.
However, as technology advances, devices are becoming smaller and more powerful. This shift creates new challenges in cable design, especially when space is at a premium. A poorly optimized ribbon cable can cause signal interference, mechanical strain, or even system failure.
That is why I want to share practical ways to optimize ribbon cables for small devices. From choosing the right materials to planning efficient layouts and selecting suitable connectors, this blog will help you create cable solutions that meet modern design demands while keeping performance and reliability at their highest level.
What Is a Ribbon Cable?
A ribbon cable is a type of electrical cable characterized by multiple parallel conductors arranged side by side in a flat, ribbon-like configuration. This design allows the cable to maintain a compact and organized form factor, making it ideal for connecting multiple points in a neat and efficient manner.
Ribbon cables typically consist of a series of round or rectangular insulated wires laid out in a row, encased in a flat, flexible insulation material. The conductors run parallel to each other, which simplifies routing and keeps wiring tidy within electronic devices.
There are several common types of ribbon cables used in electronics. One popular type is the IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) cable, which allows quick and reliable connections without stripping the insulation from individual wires. Another common variety is UL2651 jumper cables, often used for internal wiring in small devices due to their thin profile and flexibility.
The benefits of ribbon cables include their flexibility, which enables easy bending and routing within confined spaces typical of small devices. Their compact shape saves valuable space compared to round cables, facilitating more streamlined and lightweight device designs. Additionally, ribbon cables are well-suited for mass termination processes, allowing multiple conductors to be connected simultaneously using specialized connectors, which improves manufacturing efficiency and reduces the chances of wiring errors. These advantages make ribbon cables a popular choice for optimizing interconnections in small electronic devices.
What Are The Challenges Of Using Ribbon Cables In Small Devices?
When designing and working with small devices, ribbon cables offer many benefits but also come with specific challenges that must be addressed to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Understanding these challenges helps in making informed decisions and applying best practices in device design and assembly.
The first major challenge is space limitations. Small devices inherently have very tight and compact internal layouts. Ribbon cables, although flat and flexible, still require careful routing to fit within limited spaces without causing interference with other components or creating bulk that could affect the device’s form factor.
Another challenge is heat dissipation. Small devices generate heat from various internal components, and the close proximity of ribbon cables can lead to heat accumulation. Since ribbon cables often have closely packed conductors, inadequate heat dissipation might affect cable performance or accelerate material degradation.
Signal interference, specifically electromagnetic interference (EMI), is a significant concern with ribbon cables. The parallel conductor layout can cause the cable to act like an antenna, emitting or picking up noise, especially if the cable is unshielded. This can degrade signal quality in sensitive small electronics and lead to malfunction or data errors.
Lastly, mechanical wear and flexibility pose challenges. Ribbon cables, while flexible, generally bend only along their lengthwise axis. Repeated bending or improper handling can cause mechanical fatigue, conductor breakage, or connector damage. Ensuring the cable bends within its specified radius and is securely fixed to avoid undue stress is essential for device durability.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for optimizing ribbon cable usage in small devices, balancing between compactness, performance, and reliability.
Why Ribbon Cable is Ideal for Small Devices?
Ribbon cable is ideal for small devices due to several key advantages that align perfectly with the constraints and requirements of compact electronic designs.
First, ribbon cables have a flat and flexible construction, which makes them highly space-efficient. Their slim profile allows them to fit comfortably within tight spaces where traditional round cables would be bulky or difficult to route. This compactness is especially important in small devices where every millimeter of internal space counts.
Second, the flexibility of ribbon cables enables easy bending and routing around components without risking damage to the conductors. This allows for more design freedom and simplifies assembly within confined device interiors.
Another critical benefit is the ease of mass termination. Ribbon cables can be quickly and reliably connected using insulation-displacement connectors (IDC) that connect all conductors simultaneously. This reduces assembly time and the potential for wiring errors, which is valuable in manufacturing small devices efficiently.
In addition, ribbon cables contribute to improved airflow inside devices due to their flat shape. Unlike bulky round cables that can block ventilation, ribbon cables take up less volume, helping with heat dissipation and lowering the risk of overheating.
Ribbon cables are also inherently well-organized since their conductors run parallel and are color-coded in many cases. This organization simplifies troubleshooting and maintenance in small devices where access might be limited.
Finally, ribbon cables maintain good electrical performance, supporting effective data and power transmission in dense wiring environments often present in small electronics.
What Are The Key Factors For Optimizing Ribbon Cables?
When designing small electronic devices, every millimeter of space matters. Ribbon cables are often the preferred solution due to their compact and organized layout. However, simply choosing a flat cable is not enough. To ensure high performance, safety, and durability, several key factors must be considered when optimizing ribbon cables for your application. Below 6 keys are the most important aspects I focus on when helping customers design efficient and reliable ribbon cable solutions.
1.Choose the Right Pitch
The pitch, or spacing between conductors, is crucial. Common pitches include 0.5mm and 1.0mm, and the choice impacts both compactness and current capacity. A smaller pitch allows for more conductors in a tight space, improving compactness, but may limit current carrying capacity and increase crosstalk. Selecting the correct pitch balances the need for a small form factor with electrical performance.
2.Use High-Quality, UL-Certified Materials
Using UL-certified materials, such as UL2651-rated insulation, ensures the ribbon cable meets safety standards for electrical insulation and durability. High-quality materials resist wear, heat, and environmental degradation, reducing failures and maintaining long-term reliability. Certified cables provide peace of mind for both manufacturers and end users.
3.Design Custom Length and Connector Types
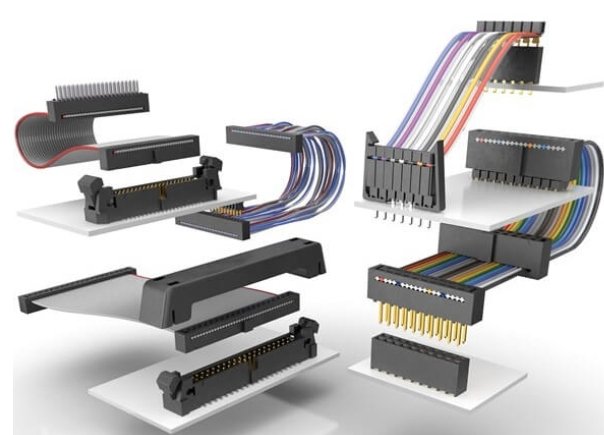
Optimizing cable length avoids excess slack that adds bulk or too tight fits that strain the cable. Custom length cables improve organization and reduce mechanical stress. Connector choice is also vital—insulation displacement connectors (IDC) allow quick mass termination, while D-SUB or custom molded connectors can provide secure, application-specific connections for small devices.
4.Implement Shielding or Twisting for EMI Protection
In high-frequency or sensitive applications, electromagnetic interference (EMI) can degrade signal quality. Shielding options such as foil or braided shields, or twisting conductors within or alongside the ribbon, help protect signals from EMI. This is important where ribbon cables run close to noise sources or sensitive circuitry.
5.Improve Flexibility with Proper Cable Selection
Ribbon cables come in standard flat types as well as ultra-flexible or round variants. Choosing cables designed for enhanced flexibility reduces mechanical stress and helps accommodate tight bends in confined spaces without damaging conductors. This improves installation ease and long-term durability.
6.Use Injection Molding for Stress Relief
Applying injection molding or overmolding around cable ends and connectors creates strain relief that protects solder joints and terminations from mechanical stress. This reduces the risk of damage during device assembly, handling, or repeated flexing in use, enhancing reliability.

What Are The Applications Of Optimized Ribbon Cables?
Optimized ribbon cables find extensive use across various industries due to their compact form factor, flexibility, and high-performance capabilities. These cables enable advanced electronic connections in space-constrained environments while maintaining signal integrity and durability. Their adaptability makes them suitable for diverse applications that demand precision and reliability.
1.Medical Devices
Optimized ribbon cables are widely used in portable monitors, diagnostic tools, and invasive medical equipment. Their small size and precise electrical characteristics support reliable signal transmission in compact, sensitive medical instruments, including endoscopy cameras, patient monitors, and catheter systems. They also offer biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization processes critical for medical applications.
2.Consumer Electronics
In devices such as printers, scanners, and drones, ribbon cables provide organized, space-saving interconnections between circuit boards and components. Their flat and flexible construction allows easy routing inside compact housings, enabling high-density wiring with efficient signal transfer for better device performance.
3.Automotive Dashboards and Infotainment
Ribbon cables are employed in modern automotive dashboards and infotainment systems where space is limited, and multiple signals including audio, video, and control data must be transmitted reliably. Their durability and flexibility help withstand vibration and thermal stresses within the vehicle environment.
4.Industrial Control Panels and Sensors
In industrial automation, ribbon cables connect control panels, sensors, and actuators where space constraints and harsh operating conditions exist. Their robustness and ability to carry numerous signals in a compact assembly make them suitable for efficient wiring in complex machinery and control systems.
These applications highlight how optimized ribbon cables contribute to improved device design, enhanced reliability, and better performance in small and demanding settings across medical, consumer, automotive, and industrial sectors.
FAQ:
Q1.How do I choose the correct pitch (spacing) for a ribbon cable in tight spaces?
A:Choosing the correct pitch (spacing) for a ribbon cable in tight spaces is essential for ensuring proper fit, reliable connections, and optimal electrical performance. The pitch refers to the center-to-center distance between adjacent conductors in the cable.
To select the right pitch, follow these key points:
a.Match Connector and Cable Pitch:
The pitch of the ribbon cable must correspond precisely to the pitch of the connectors or headers it interfaces with. Common connector pitches are usually twice the ribbon cable pitch. For example, a 1.27mm (0.05 inch) pitch connector typically pairs with a 0.635mm (0.025 inch) pitch ribbon cable. Always verify the mating parts’ specifications.
b.Consider Space and Current Requirements:
Smaller pitches (e.g., 0.5mm or 0.635mm) allow more conductors in less space, ideal for very compact devices. However, smaller spacing reduces the conductor size and current carrying capacity. Larger pitches (1mm or 1.27mm) support more current per conductor but occupy more space. Choose a pitch that balances compactness with electrical needs.
c.Use Measurement or Formula If Needed:
If unsure, measure the total cable width and count the number of conductors. Use the formula:

This calculation helps determine the actual conductor spacing relevant for fitting tight connectors.
d.Account for Manufacturing and Handling Tolerances:
Tight spaces require precise cable and connector tolerances. When choosing very fine pitch ribbons (under 0.5mm), consider potential handling difficulty and reliability risks.
Q2.What is the best ribbon cable type for high-density connectors?
A:The best ribbon cable type for high-density connectors is typically IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) ribbon cable. IDC ribbon cables feature a flat multiconductor design that allows for mass termination using IDC connectors, which pierce the insulation with sharp blades to contact all conductors simultaneously. This enables quick, reliable, and cost-effective assembly for high-density pin configurations.
In addition, certain variants like folded flat ribbon cables offer enhanced flexibility in tight spaces while retaining high conductor counts, making them suitable for dense layouts. For extremely space-constrained or high-frequency applications, FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) or FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) cables paired with matching high-density connectors provide even slimmer profiles and greater flexibility.
In terms of connector compatibility, common high-density connectors used with ribbon cables include:
- BT 224 (IDC) connectors, standardized for 0.1-inch (2.54 mm) pitch ribbon cables, popular for computer and consumer electronics.
- D-Subminiature connectors, available in higher pin counts, suitable for complex systems.
- DIN 41612 connectors, widely used in industrial and telecom equipment.
- Picoflex connectors and similar low-profile connectors optimized for very compact, high-density board-to-board or wire-to-board connections.
Q3.Can ribbon cables be customized in length, color, and labeling?
A:Yes, ribbon cables can be customized in several ways to fit specific application needs
- Length: Ribbon cables can be made to any custom length, allowing you to avoid excess slack that wastes space or overly tight cables that cause stress. Custom lengths ensure a perfect fit within device enclosures and assemblies.
- Color: Custom color coding is commonly offered, either by manufacturing the individual conductors in specific colors or applying colored jackets or stripes. This helps with conductor identification, correct orientation, and easier troubleshooting.
- Labeling: Ribbon cables can include custom printing, edge markings, or colored stripes to mark the first conductor for correct connector alignment. Additional labels or markings can help identify cable functions or wire groups, which is especially useful in complex assemblies.
Custom ribbon cables can also include variations like folded configurations to fit tight spaces, molded connectors or strain reliefs, and special materials for environmental resistance. These customizable options make ribbon cables versatile solutions tailored to meet the space, electrical, and mechanical requirements of your project.
Q4.What is the difference between IDC ribbon cables and jumper cables?
A:IDC ribbon cables and jumper cables are both used for internal wiring in electronic devices, but they serve different purposes and are constructed differently.
IDC Ribbon Cables
IDC stands for Insulation Displacement Connector. An IDC ribbon cable is a flat, multi-conductor cable where the wires are positioned side by side in a ribbon-like layout. These cables are terminated with IDC connectors using a special technique that pierces the insulation to make contact with the conductors, without needing to strip the wire.
- Best for: High-density connections, such as connecting PCBs, LCDs, or control panels.
- Advantages: Quick mass termination, clean alignment, ideal for compact spaces.
- Common pitch sizes: 0.635 mm, 1.27 mm (e.g., UL2651).
Jumper Cables
Jumper cables are typically individual or a small number of wires bundled together, often with crimped connectors or pins at the ends. They are used to connect two points on a circuit, usually for signal or power transfer.
- Best for: Prototyping, low-volume connections, or bridging PCB pins.
- Advantages: Flexible, easy to replace, customizable in small quantities.
- Commonly used: On breadboards, Arduino, or development boards.
Q5.What materials are best for insulation and durability in miniaturized ribbon cable systems?
A:When designing miniaturized ribbon cable systems, choosing the right insulation material is critical for ensuring electrical safety, flexibility, heat resistance, and long-term durability. Below are the 5 best materials commonly used for insulation in compact ribbon cables, especially in precision and high-density applications:
a. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Best for: General-purpose use
Advantages: Low cost, flexible, flame-retardant, and easy to process
Limitations: Limited temperature and chemical resistance
Typical use: Consumer electronics, computer peripherals
Yihetai Note: We use high-quality UL-certified PVC in many of our UL2651 ribbon cables for consistent performance in small devices.
b. Polyethylene (PE)
Best for: High-frequency, low-loss signal transmission
Advantages: Excellent electrical properties, low dielectric constant
Limitations: Less flexible than PVC
Typical use: Data communication, signal cables in compact control units
c. Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
Best for: Flexibility and mechanical durability
Advantages: High flexibility, excellent abrasion resistance, good for repeated bending
Limitations: More expensive than PVC
Typical use: Wearable devices, robotics, mobile medical equipment
d. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene / Teflon
Best for: Harsh environments
Advantages: High temperature resistance (up to 260°C), chemical and flame resistance, low friction
Limitations: Higher cost, more difficult to process
Typical use: Aerospace, medical instruments, automotive electronics
e. Polyimide (e.g., Kapton)
Best for: Extreme miniaturization and thermal environments
Advantages: Ultra-thin, high thermal stability, chemical resistance
Limitations: Fragile and expensive
Typical use: Space-constrained PCBs, FPCs (Flexible Printed Circuits)
Q6.Can I use ribbon cables in medical or wearable electronics? What should I consider?
A:Yes, ribbon cables can be used in medical and wearable electronics, but certain important considerations must be taken into account to ensure safety, reliability, and user comfort. 加粗
Medical devices, including portable monitors and diagnostic tools, often require cables that meet stringent regulatory standards for biocompatibility, electrical safety, and durability. Ribbon cables used in such environments need to have high-quality insulation and materials that resist moisture, chemicals, and sterilization processes. Connectors and cables must be ruggedized to withstand handling, vibration, and potential exposure to fluids. EMI shielding is crucial to prevent interference with sensitive medical electronics and maintain signal integrity.
In wearable electronics, flexibility and miniaturization are paramount. Ribbon cables must be ultra-thin, lightweight, and capable of bending repeatedly without breaking. Comfort is also key, so cables should be designed with smooth surfaces and soft materials where contact with the skin occurs. Durable materials that can withstand sweat, movement, and environmental exposure are needed. Special connectors like spring-loaded (pogo pin) types offer easy mating and high durability for charging or data transfer in wearable applications.
In both fields, proper strain relief, encapsulation, and environmental sealing extend cable lifespan and reliability. Selecting cables and connectors compatible with regulatory standards such as IEC 60601-1 for medical devices ensures compliance and safety.
How Yihetai Can Support Your Ribbon Cable Projects
When it comes to developing ribbon cable systems for small devices, choosing the right manufacturing partner can make all the difference. At Yihetai, we go beyond basic production. We offer expert guidance, flexible capabilities, and full technical support throughout the entire project. Whether you are building a high-end medical device or launching a new generation of compact electronics, here is how we can support your success.
1.Over 23 Years of Cable Assembly Expertise
With more than two decades of industry experience, we have built a strong foundation in ribbon cable and wire harness design. Our team has supported clients across a wide range of industries including automotive, industrial automation, consumer electronics, and healthcare. This gives us the insight to deliver optimized solutions for your unique needs.
2.Custom Design, Material Selection, and In-House Production
Yihetai handles everything internally from raw material development to final assembly. This allows us to offer fully customized ribbon cable solutions tailored to your design, size, and performance requirements. Our in-house process ensures better quality control, faster lead times, and more flexibility for design changes.
3.Certified Quality with UL and IATF16949 Compliance
We manufacture all products under strict quality standards. Our ribbon cables are UL certified and our factory is IATF16949 certified for automotive-grade production. These certifications demonstrate our commitment to consistent quality, safety, and reliability across all orders.
4.Flexible Production Capacity from Prototypes to High Volumes
Whether you need a small run for testing or large-scale production for commercial release, we are equipped to handle it. Our manufacturing setup supports both low-volume customization and high-volume output with the same level of precision and attention to detail.
5.Comprehensive Electrical Testing and Quality Assurance
Every ribbon cable undergoes complete electrical testing including continuity, insulation resistance, and visual inspection. We maintain full product traceability and enforce strict quality control procedures at each stage of production to ensure that your cables perform reliably under real-world conditions.
Conclusion
Optimizing ribbon cables for small devices is more than just managing space. It is about ensuring consistent performance, minimizing signal issues, and creating a reliable connection that supports the long-term success of your product. As devices become smaller and more advanced, paying attention to the details of cable design becomes increasingly important.
From the choice of materials to the layout and connectors, every decision plays a role in the final outcome. That is why my advice is to always partner with a manufacturer who has real experience and understands the unique challenges of compact electronic designs.
At Yihetai, we specialize in customized ribbon cable assemblies and wire harness solutions built to match your exact requirements. Whether you are developing a new product or improving an existing one, we are ready to support you.
Feel free to reach out to me for a consultation or to discuss a custom solution for your project. I would be happy to help.


